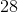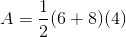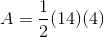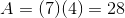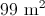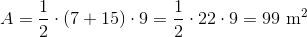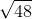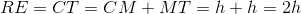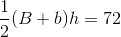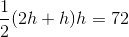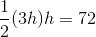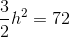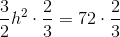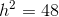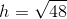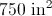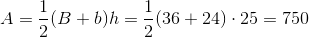All SSAT Middle Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Trapezoid
Find the area of the trapezoid:
The area of a trapezoid can be determined using the equation 
Example Question #33 : Geometry
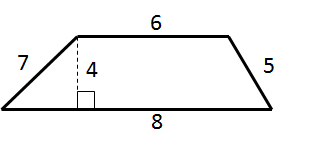
What is the area of the trapezoid?
To find the area of a trapezoid, multiply the sum of the bases (the parallel sides) by the height (the perpendicular distance between the bases), and then divide by 2.
Example Question #1 : Trapezoids
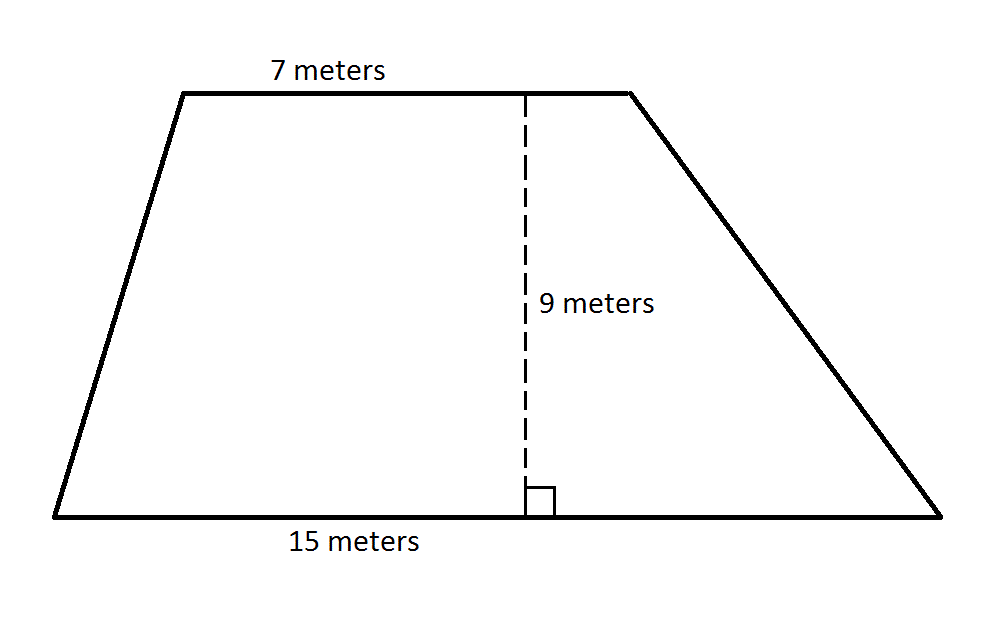
The above diagram depicts a rectangle 





The length of a leg of 

Since the triangle is isosceles, then 



Therefore, the orange region is a trapezoid with bases 


This is the length of one leg of the triangle.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Trapezoid
A trapezoid has a height of 


Use the following formula, with 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Trapezoid
What is the area of a trapezoid with height 20 inches and bases of length 100 and 200?
Set 


The area of a trapezoid can be found using this formula:
The area is 3,000 square inches.
Example Question #401 : Ssat Middle Level Quantitative (Math)

Figure NOT drawn to scale.
Evaluate 
By the Segment Addition Postulate,
Example Question #1 : How To Find Length Of A Line
A right triangle has one leg with a length of 6 feet and a hypotenuse of 10 feet. What is the length of the other leg?
In geometry, a right angle triangle can occur with the ratio of 
When you know the length of two sides of a right angle triangle like this, you can calculate the third side using this ratio.
Here, the ratio is:
This is double the 
Another way to solve is to use the Pythagorean Theorem: 
We know that one leg is 6 feet and the hypotenuse is 10 feet.
Example Question #2 : How To Find Length Of A Line
The radius of a circle is 6 inches. What is one-third of the diameter?
If the radius is equal to 6 inches, then the diameter will be double that value, or 12 inches. One-third of 12 is 4, which is therefore the correct answer.
Example Question #214 : Geometry
A right triangle has one leg with length 

Since we are dealing with a right triangle, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem:

where 




Substituting values into the Theorem:
Example Question #3 : How To Find Length Of A Line
Line 





A line that is bisected is split into two segments of equal length. Therefore, if line 


Consequently, bisecting line segment 

Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Middle Level Math Resources