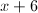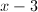All SAT II Math I Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #11 : Simplifying Expressions
Factor completely:
The grouping technique works here:
The first factor is the difference of squares and can be factored further accordingly:
Example Question #11 : Simplifying Expressions
Factor completely:
The polynomial is prime.
The polynomial is prime.
Since the first term is a perfect cube, the factoring pattern we are looking to take advantage of is the difference of cubes pattern. However, 243 is not a perfect cube of an integer , so the factoring pattern cannot be applied. No other pattern fits, so the polynomial is a prime.
Example Question #123 : Single Variable Algebra
Exponentiate:
Vertical multiplication is perhaps the easiest way to multiply trinomials.
Example Question #14 : Simplifying Expressions
Exponentiate:
The difference of two terms can be cubed using the pattern
Where :
Example Question #124 : Single Variable Algebra
How many of the following are prime factors of ?
I)
II)
III)
IV)
Three
None
Two
One
Four
Three
Factor all the way to its prime factorization.
can be factored as the difference of two perfect square terms as follows:
is a factor, and, as the sum of squares, it is a prime. is also a factor, but it is not a prime factor - it can be factored as the difference of two perfect square terms. We continue:
Therefore, of the given four choices, only is not a factor, so the correct response is three.
Example Question #42 : Binomials
For all values , which of the following is equivalent to the expression above?
First, factor the numerator. We need factors that multiply to and add to .
We can plug the factored terms into the original expression.
Note that appears in both the numerator and the denominator. This allows us to cancel the terms.
This is our final answer.
Example Question #16 : Simplifying Expressions
Simplify the following expression:
When simplifying an equation,you must find a common factor for all values in the equation, including both sides.
and, can all be divided by so divide them all at once
.
This leaves you with
.
Example Question #21 : Simplifying Expressions
Simplify the expression
Already in simplest form
Simplify the numerator by multiplying in the term
Cancel out like terms in the numerator and denominator.
Example Question #22 : Simplifying Expressions
Simplify:
Rewrite the denominator of the second fraction using a power.
Using the subtraction rule of exponents, we can simplify this as one term.
The expression becomes:
Apply the addition rule of exponents.
The answer is:
Example Question #23 : Simplifying Expressions
Factor an in the numerator to get:
We can now cancel out from the numerator and denominator leaving the answer.
Certified Tutor
All SAT II Math I Resources



























































![=\left ( 9y^{2} + 1 \right )\left [ \left (3y \right ) ^{2} - 1^{2} \right ]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/211029/gif.latex)