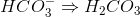All SAT II Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Reactions And Equilibrium
Which of the following cannot act as a Bronsted-Lowry base (proton recipient) in aqueous solution?
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:



Example Question #2 : Reactions And Equilibrium
A scientist makes a solution by adding 0.2 grams of 
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:






Taryn
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
University of Florida, Bachelor of Science, Biology, General. University of Florida, Bachelor of Science, Business Administra...
Geo
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
Church Teachers College, Bachelor, Science Education. University College of the Carib, Bachelor in Business Administration, B...
All SAT II Chemistry Resources
Popular Subjects
LSAT Tutors in Washington DC, French Tutors in New York City, Physics Tutors in Atlanta, English Tutors in Boston, English Tutors in Los Angeles, Statistics Tutors in San Diego, GMAT Tutors in Dallas Fort Worth, Reading Tutors in Houston, ACT Tutors in Boston, ISEE Tutors in New York City
Popular Courses & Classes
Spanish Courses & Classes in Houston, LSAT Courses & Classes in Seattle, Spanish Courses & Classes in New York City, ISEE Courses & Classes in Boston, LSAT Courses & Classes in Washington DC, LSAT Courses & Classes in New York City, ACT Courses & Classes in Miami, ACT Courses & Classes in Houston, SAT Courses & Classes in Houston, LSAT Courses & Classes in Philadelphia
Popular Test Prep
ACT Test Prep in Houston, GRE Test Prep in Seattle, LSAT Test Prep in Phoenix, GRE Test Prep in Phoenix, SSAT Test Prep in Atlanta, MCAT Test Prep in San Francisco-Bay Area, GMAT Test Prep in Seattle, ACT Test Prep in San Francisco-Bay Area, LSAT Test Prep in Chicago, LSAT Test Prep in New York City