All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Identification By Structure
Identify the common name of the fatty acid shown here.

Arachidonic acid
Oleic acid
Linoleic acid
Palmitic ccid
Myristic acid
Oleic acid
Oleic acid is a fatty acid consisting of 18 carbon molecules and a single unsaturated (double) bond after carbon 9, as pictured.
Example Question #252 : Organic Chemistry
What type of lipid is shown below?

Fatty acid
Phosphatidylcholine
Triglyceride
Phospholipid
Steroid
Triglyceride
A triglyceride consists of three fatty acid chains bound to a glycerol backbone via ester bonds, as shown by the pictured structure.
Example Question #5 : Help With Organic Lipids
Three fatty acid chains can be bound to a glycerol backbone via ester bonds to form a triglyceride. What type of chemical reaction is this?
Oxidation-reduction
Hydrolysis
Condensation
Hoffman elimination
Markovnikov
Condensation
The reaction described is an esterification in which water is a product—as is characteristic of a condensation reaction—and in which an ester bond is formed to connect the fatty acid chain and the glycerol molecule.
Example Question #5 : Biological Molecules
An unknown molecule was found to have a molecular formula of 
None of these
fatty acid
triaclyglycerol
steroid
None of these
This question is a little bit tricky. At first glance, we would jump to the conclusion that this molecule is a long hydrocarbon chain attached to a carboxylic acid and, therefore, a fatty acid. The premise is correct. However, our conclusion is false because, by convention, a fatty acid must contain a carbon chain of at least 12 carbons. The given formula does not match the description for a steroid or triacylglycerol. The correct answer is none of these.
Example Question #2 : Help With Organic Lipids
What is the primary biological function of a fatty acid?
To serve as a medium for the derivation of other important lipids
All of these
To serve as a water barrier on the outside of leaves and feathers
To serve as a medium for energy storage
To serve as a medium for the derivation of other important lipids
The primary biological function of a fatty acid is to serve as a medium for the derivation of other important lipids such as waxes, triacylglycerols, phospholipids, and other necessary lipids.
Example Question #3 : Help With Organic Lipids
Before the advent of synthetic soap, hand soap was made from animal fat, namely triacylglycerols. What property of triacylglycerols make them an ideal component in hand soap?
The ability to engulf dirt/grease on skin
None of these
The ability to engulf and digest harmful bacteria on skin
The presence of hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads that work to dissolve into and remove dirt/grease on the skin
The presence of hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads that work to dissolve into and remove dirt/grease on the skin
A triacylglycerol is derived from the hydrolysis of glycerols and fatty acids. Triacylglycerols have hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails and hydrophilic heads (amphipathic). The hydrophobic tails dissolve into dirt/grease on the skin while the hydrophilic tails work with running water to suspend and remove the dissolved impurities.
Example Question #253 : Organic Chemistry
Based on the formula and structure of this molecule, this molecule can be classified as a __________.
protein
complex sugar
wax
fatty acid
wax
The correct answer is the lipid, wax. Lipids can often be identified based on their structure alone. The general structure of wax is an ester with two long carbon chains on each end of the ester, as seen in this problem. Additionally, fatty acids can be identified simply as long carbon chains with a carboxylic acid on one end, while the general structure of steroids can be seen as four connected hydrocarbon rings.
Example Question #11 : Help With Organic Lipids
The following terpene is classified as which of the following?

Hemiterpene
Monoterpene
Diterpene
Monoterpenoid
Eicosanoid
Monoterpene
The molecule's skeletal structure contains two isoprene (2-methylbutyl) units, and therefore the molecule is a monoterpene.
Example Question #12 : Help With Organic Lipids

Which of these two fatty acids has the lower melting point and why?
Stearic acid, because it contains more cis double bonds.
They have the same melting point since both have 18 carbons.
Stearic acid, because it contains fewer cis double bonds.
Alpha-linolenic acid, because it contains fewer cis double bonds.
Alpha-linolenic acid, because it contains more cis double bonds.
Alpha-linolenic acid, because it contains more cis double bonds.
Fatty acids that contain a higher degree of unsaturation (more alkene bonds) will introduce more "kinks" into the hydrocarbon chain. This "kinked" chain does not stack nicely with other fatty acids of its kind and therefore are more likely to slip past each other at lower temperatures. This is primarily due to the van der Waals forces within the unsaturated fatty acids being disrupted with the introduction of double bonds. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids generally have a lower melting point than saturated fatty acids.
Example Question #1 : Help With Organic Carbohydrates
Chemists and biochemists have many ways of representing sugars. Glucose, the most common hexose, is shown below in various linear and cyclic projections. Using the linear and cyclic projection of your choice, can you indicate which colored oxygen in the linear form corresponds to the circled hemiacetal oxygen once the cyclization reaction is complete?
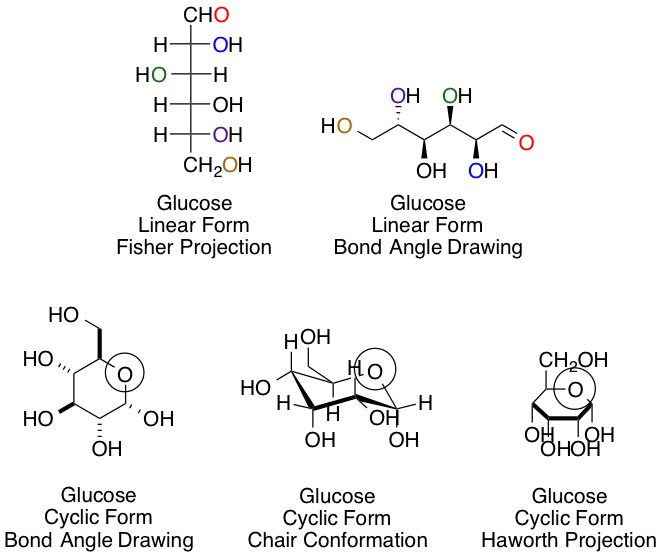
Purple
Green
Red
Yellow
Blue
Purple
This answer, regardless of your preference of projection type, is easiest to obtain using arrow pushing for the cyclization reaction to keep track of each carbon and oxygen:

The purple carbon in the linear projection ends in the circled hemiacetal position.
Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources





