All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #2 : Identifying Electron Donating Groups
Which of the given compounds is not a Lewis acid?
All of these are Lewis acids
A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor.
The carbocation is clearly trying to accept electrons due to the positive charge. 

The correct answer has a lone pair on the nitrogen, and thus has electrons to donate and as a Lewis base. 
Example Question #1 : Identifying Electron Withdrawing Groups
Which of the following R groups would increase the rate of the following substitution reaction?
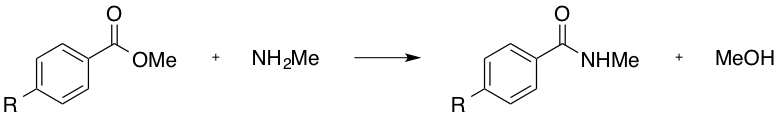
The above reaction would more readily proceed if the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon were enhanced. This may be achieved through electron withdrawal via the R group.
The ether (-OMe), the methyl (-Me), and the hydroxyl (-OH), would all produce a electron-donating effect, and are thus incorrect answers.
The nitro group (-NO2), and the positively charged, tetra-substituted amino group (consider the structure once this trimethyl amino group is connected to the aryl ring) are both electron-withdrawing. As the trimethyl amino group will have an overall positive charge (and the nitro group is neutral overall), the trimethyl amino group is the stronger electron-withdrawing moiety, and is thus the correct answer.
Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources













