All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #3 : Help With Grignard Reactions
What is the product of the reaction shown?


I
III
IV
II
I
Step 1 converts the carboxylic acid into an ester.
Step 2 adds two equivalents of Grignard reagent: one to turn the molecule into acetone, and a second one to turn it into tert-butoxide. There is no way to stop the reaction after the first addition of Grignard reagent.
Step 3 will neutralize the base, leaving only t-butyl alcohol (I).
Example Question #1 : Help With Aldol Condensation

Determine the major product of the given intramolecular aldol reaction.

I
None of these
III
IV
II
II
Keep in mind the following principles: Cyclization is favored when a five/six-member ring may be formed. Addition at an aldehyde is favored relative to the same reaction at a ketone.
As a result, abstraction of a hydrogen bound to carbon 6 (an alpha-carbon) is favored since the resulting carbanion may attack the aldehyde (carbon 1) to form a six-member ring, resulting in compound II. Compound I results from abstracting a hydrogen from carbon 2, generating a carbanion which may then attack the ketone. Based on the latter of the above principles, this is a minor product.
Example Question #651 : Organic Chemistry
What is the final organic product of the reaction shown?


V
IV
III
I
II
I
First step: Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene
Second step: Formation of enolate
Third step: aldol addition (enolate attacks carbonyl carbon in benzaldehyde)
Fourth step: neutralization of anion and dehydration forming alkene
Example Question #3 : Carbonyl Reactions

What is the product of this reaction?

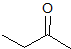

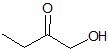
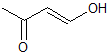

This is a classic esterification reaction. Esterfication occurs when a carboxylic acid and an alcohol are reacted together. Only one answer choice is an ester.
Example Question #11 : Specific Reactions And Named Reactions
What is the final organic product of the reaction shown?


I
IV
V
II
III
III
First step: esterification
Second step: reduction
Third step: neutralization
Fourth step: oxidation to aldehyde
Fifth step: alkene metathesis
Example Question #652 : Organic Chemistry
All of the following are characteristics of a Wittig reaction except __________.
it results in the formation of a carbon-carbon double bond
it involves the reaction of a phosphonium ylide with a carbonyl
it produces a trialkylphosphine oxide or triarylphosphine oxide as a by-product
it results in the exclusive formation of trans double bonds
it proceeds through a phosphaoxetane intermediate
it results in the exclusive formation of trans double bonds
The Wittig reaction involves the reaction of a phosphonium ylide (generated by treating a phosphonium salt with a strong base) with a ketone or aldehyde.
The reaction proceeds through a phosphaoxetane (4-membered ring containing both phosphorus and oxygen) intermediate to generate a new compound containing a carbon-carbon double bond, plus a phosphine oxide byproduct. It does not form trans double bonds exclusively; sometimes, a mixture of cis and trans isomers are obtained, and sometimes the cis isomer is the predominant product.
Example Question #653 : Organic Chemistry
Which of the following best summarizes the haloform reaction?
An alkyl halide reacts first with the phthalimide ion, then with
The enolate of a dicarbonyl compound attacks a beta carbon of an alkene
The enolate of an ester attacks another ester
A carboxylic acid reacts first with 
A methyl ketone is treated with iodine and
A methyl ketone is treated with iodine and
The haloform reaction requires a carbonyl with a terminal alpha carbon. A hydrogen gets abstracted, and the enolate is formed. A halogen attacks the alpha carbon, and the ketone is reformed. This occurs three more times until the carbon has bonds to three halogens. Then the carbon leaves, forming a carbanion, and the base attacks the carbonyl carbon. An ester is formed.
Example Question #2 : Carbonyl Reactions
Which of the following results in a single ketone product following acid catalyzed hydration?
5-decyne
4-decyne
2-decyne
3-decyne
None of these answers
5-decyne
During acid catalyzed hydration, a hydroxy group replaces one of the bonds in the triple bond and a double bond is formed. This is called an enol. The enol naturally turns into a ketone in a process called tautomerization. The hydroxy group can attach to either carbon across the double bond, and naming is done so that substituents have the lowest numbers. Only on 5-decyne will result in a single product, as no matter which carbon the hydroxy group bonds to, it is still on carbon 5. Thus, the only final product is 5-decone.
The other answer options will still react, but will form multiple products due to lack of symmetry.
Example Question #3 : Carbonyl Reactions
What is the product of the reaction shown?

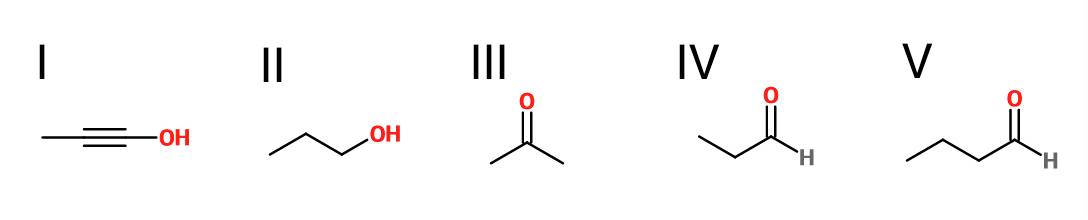
II
I
IV
V
III
IV
First step: bromination across the double bond
Second step: double dehydrohalogenation and removal of terminal alkyne hydrogen
Third step: neutralization of the molecule
Fourth/fifth step: hydroboration/oxidation, followed by keto/enol tautomerization
Example Question #654 : Organic Chemistry
What is a product when propyl-butanoate undergoes saponification?
Propanol
Butanol
Propanoic acid
Butyl propanoate
None of these
Propanol
When naming esters, the root word in the name describes the carbon chain that carries the carbonyl. Saponification describes the breaking up of an ester. This yields an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. The chain with the carbonyl is butyl, so the carboxylic acid will be butanoic acid. That means the side with the alcohol will be propanol.
Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources







