All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #123 : Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry, And Metabolism
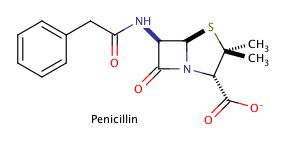
Shown above is the chemical structure for penicillin, a common prescription drug. How many chiral carbons does penicillin have?
One
Two
Three
Zero
Five
Three
The correct answer is three. The key to finding chiral carbons is to look for carbons that are attached to four different substituents. We can immediately eliminate any carbons that are involved in double bonds, or that have two hydrogens attached. Given this, we find that there are three chiral carbons. Note that carbon chains of varying content will qualify as different substituents, allowing chiral carbons to bond to two other carbons.
Example Question #2 : Help With Enantiomers

Which two of the molecules shown are enantiomers?
I and II
II and III
III and IV
I and III
II and IV
I and III
The enantiomer of a molecule with multiple chiral centers is formed through configurational inversion at every chiral center. By rotating the ring of molecule III 180 degrees about the bond connected to its carbon chain, it is seen that molecules I and III are constitutionally identical with opposite configurations at every chiral center. These compounds are enantiomers. Tip: mental visualization of bond rotations and other transformations is among the most common difficulties experienced in organic chemistry courses. The use of a molecular modeling kit may greatly assist in molecular visualization. Molecules I and II are the same, just rotated 180 degrees.
Example Question #4 : Isomers
Which of the following best describes an S-enantiomer?
Levorotatory
Rotates light clockwise
Dextrorotatory
None of these
None of these
S configuration deals with the arrangement of atoms around a chiral center. Levorotatory and dextrorotatory refer to the rotation of light (either clockwise or counter clockwise), which can only be calculated experimentally using a polarimeter to create plane polarized light. "Rotates light clockwise" is simply another way to say dextrorotatory. Therefore, none of the answer choices are correct.
Example Question #8 : Isomers

How many stereoisomers exist for the given compound?
In this question, we're presented with the structure of a compound and we're asked to determine how many stereoisomers for this compound exists. It's important to remember that stereoisomers are compounds that have the same chemical formula and the same connectivity between its atoms, but what sets them apart is how their atoms are oriented in space.
When looking at the structure of the molecule in the question, we can see that there are two chiral carbons (carbons with four different substituents bound). A chiral carbon can have its substituents bound in two different ways, either R or S. Since each chiral carbon has two possible configurations of its atoms, the total numbers of possible stereoisomers is equal to 


Example Question #1 : Help With Enantiomers

How many different stereoisomer orientations are possible for the given molecule?
There are 5 different chiral centers in the molecule as shown below:

In order for a carbon to be a chiral center, it must be bonded to 4 different groups. The total number of possible stereoisomers is equal to 
Example Question #2 : Help With Enantiomers

How many chiral centers does the given molecule have?
There are 8 chiral centers which are marked below:

Carbon atoms need to be attached to 4 different groups to have a chiral center. Keep in mind that carbon atoms with a double bond can never be chiral. Looking at chiral center 1, the carbon is bonded to an alcohol group, a hydrogen atom, and two hydrocarbon groups. The hydrocarbon group clockwise is not identical to the hydrocarbon group counterclockwise. So this carbon would be considered bonded to 4 different groups making it chiral.
Example Question #3 : Help With Enantiomers

In the given molecule, what are the orientations of the top and bottom carbons respectively?
R,S
R,R
S,R
S,S
R,R
The orientation of the chiral center is based on what the carbon is bonded to. The heaviest atom that the carbon is bonded is given higher priority.
Top: Bottom:
Bottom:
For the top carbon the oxygen is the heaviest, so it receives a 1, with the hydrogen as the least important group 4. The least priority group should be placed in the back, such as shown in the bottom example, before determining clockwise or counterclockwise orientation. For the bottom section, going from most important to least important groups, while ignoring the least important group, you get clock wise or R orientation.
Interpreting the top carbon is different because the least important group is not in the back. Reading from high to low priority, while the hydrogen is in the front, gives a S configuration (ignore the 4th priority group when rotating). Since the hydrogen group is opposite from where it should be, the orientation is opposite as well.
Example Question #31 : Stereochemistry
What is the orientation of the given molecule?
Trans
R
S
Cis
S
Label the priority of bonded groups first.

Moving from first to second to third, which ignoring the 4th important group, gives a counterclockwise direction, or S.
Example Question #381 : Organic Chemistry
Isomers that are nonsuperimposeable mirror images of each other are called __________.
conformers
diastereomers
constitutional isomers
enantiomers
enantiomers
Enantiomers are chiral isomers of the same molecule that are mirror images of one another. Because of this characteristic, enantiomers cannot be placed on top of one another (superimposed) and yield the same molecule.
Example Question #382 : Organic Chemistry

How many stereocenters does the molecular framework of cholic acid (shown) have?

There are 11 stereocenters, because here there are 11 asymmetric carbons and no E/Z isomerisms, nor planes of symmetry.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources