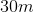All MCAT Physical Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #11 : Mirrors And Lenses
A compound microscope consists of an eyepiece with an angular magnification of 25 and an objective lens of unknown focal length. If the length of the microscope tube is 25cm, what magnitude of objective focal length is necessary to achieve an overall magnification of 500?
Relevant equations:






Given:
Step 1: Plug the expression for 

Step 2: Rearrange to isolate the unknown,
Step 3: Plug in given quantities, taking the absolute value to find the magnitude of 
Example Question #1 : Combining Lenses
What diameter of telescope objective lens is necessary to resolve two stars that primarily emit 600nm light and have an angular separation of 
Relevant equations:



Step 1: Rearrange equation to isolate the unknown, 
Step 2: Plug in the given numbers for wavelength and angular separation:
Example Question #11 : Optics
A man stands ten meters away from a converging mirror with a focal length of two meters. What is true of the image he sees?
His image is real, inverted, and minimized
His image is virtual, upright, and minimized
His image is virtual, upright, and magnified
His image is real, upright, and magnified
His image is real, inverted, and magnified
His image is real, inverted, and minimized
The first thing to consider when answering this question is the fact that real images are always inverted and virtual images are always upright. Once you have determined one or the other, two answer choices can be eliminated.
The first equation that is necessary for this question is 
From this we can determine that 


The second equation to consider is for magnification: 
If the absolute value of 
We would expect the image to be minimized.
Example Question #1 : Types Of Image
For a nearsighted person, the image of a distant object is formed __________.
in front of the retina, and corrected using a diverging lens
behind the retina, and corrected using a diverging lens
in front of the retina, and corrected using a converging lens
behind the retina, and corrected using a converging lens
in front of the retina, and corrected using a diverging lens
In nearsightedness, the person cannot see far objects due to increased refraction. This causes the image to be formed in front of the retina. This condition is corrected using a diverging lens to compensate for the "over refraction" by the deformed cornea.
Example Question #12 : Mirrors And Lenses
An object is placed 50cm in front of a converging lens whose focal length is 20cm. Which of the following best describes the image that is formed?
Smaller than the object and real
Smaller than the object and virtual
Larger than the object and virtual
Larger than the object and real
The same size as the object and virtual
Smaller than the object and real
Relevant equations:
Step 1: Plug in the given focal length and object distance to find the image distance:
Step 2: Find the magnification and orientation of the image:
A negative magnification means the image is inverted, and therefore real. A magnification smaller than 1 means the image is smaller than the object.
The following result is true, in general, for converging lenses: if the object is outside 
Example Question #191 : Mcat Physical Sciences
Jimmy is farsighted and uses a convex lens to correct his vision. Wendy is nearsighted and uses a concave lens to correct her vision. They both wear glasses. During a camping trip, they notice they do not have any matches, and decide to use their glasses to start the fire. Whose glasses could be used to start the fire?
Jimmy
Wendy
Neither glasses would work
Both glasses would work equally well
Jimmy
This question deals with an application of optics. In this case we have a farsighted person and a near sighted person. The farsighted person would use a convex lens, which is a converging lens. This would allow all of the rays of light to converge on a single point, allowing them to heat the object up and start a fire. Wendy’s glasses are diverging lenses, which would cause the rays to separate.
All MCAT Physical Resources