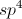All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #42 : General Chemistry
For the compound shown below, the hybridization for carbon A is __________ and the hybridization for carbon B is __________.

Carbon A is hybridized because this carbon is only bonded to two other atoms. Carbon B is bonded to four atoms, and would therefore be hybridized.
Keep in mind that a carbon involved in a triple bond will always be hybridized, a carbon involved in a double bond will be hybridized, and a carbon involved only in single bonds will be hybridized.
Example Question #21 : Covalent Bonds And Hybrid Orbitals
Which compound contains the most stable carbon bonds?
Methane
Carbon dioxide
Acetone
Ethene
Carbon dioxide
The stability of a bond can be compared to others by determining the hybridization of the bond. It helps to remember that the bond with the most s character is considered the most stable.
Carbon dioxide has a carbon that is connected to two oxygens by two double bonds. This means that the carbon has sp hybridization. Since the bond has 50% s character, it is the most stable out of the available compounds.
Methane contains only single bonds and will have an sp3 hybridized carbon, with only 25% s character. Acetone and ethene each contain one double bond and will contain an sp2 hybridized carbon with 33% s character.
Example Question #12 : Carbonyl Reactants
The compound below is reacted with . What is the final hybridization around the initially chiral center carbon when the reaction is complete?

The initially chiral carbon has an hybridization. Once treated with ,an oxidizing agent, the secondary alcohol in the compound is oxidized to a ketone. The central carbon is no longer a chiral center (a carbon with a double bond cannot be chiral), and the double bond (pi-bond) formed between carbon and oxygen gives the molecule an hybridization.
hybridization is formed with triple bonds, and an hybridization does not exist.
Example Question #51 : Molecular Properties
Which compound will have the highest bond energy?
The carbon-carbon bond in ethane.
The carbon-carbon bond in benzene.
The carbon-hydrogen bond in methane.
The carbon-carbon bond in ethene
The carbon-carbon bond in ethene
In organic chemistry, the trend is that bond length is inversely proportional to bond energy. Shorter bonds result in a higher bond energy. The double bond in ethene is the shortest bond out of all the others. As a result, it has the highest bond energy.
Note that in benzene there are three double bonds and three single bonds between carbons, however, resonance means that each of these only has partial double bond character, and is therefore longer than a pure double bond.
Example Question #52 : Molecular Properties
A carbon-carbon single bond has an average length of 1.54 Angstroms. A carbon-carbon double bond has an average length of 1.33 Angstroms. Finally, a carbon-carbon triple bond has an average length of 1.20 Angstroms. For the allyl cation shown below, what is the average carbon-carbon bond length?

The allyl cation involves resonance, as the double bond is delocalized; thus, each carbon-carbon bond will have an identical length somewhere between a pure single and pure double bond. The average bond length will be the average of a single bond and double bond, which is 1.44 Angstroms.
Example Question #22 : Covalent Bonds And Hybrid Orbitals
Which compound has the largest bond energy between carbons?
Ethyne
Benzene
1,3-butadiene
Propane
Ethyne
It helps to remember that bond energy is inversely proportional to bond length. In other words, the shorter the bond, the higher the bond energy.
Bond length is shortened when pi bonds are involved, so double and triple bonds are much shorter than simple sigma bonds. The bond length between the carbons in ethyne is the shortest out of all options because they are triple bonded to one another. This also makes it the most stable bond, and gives it the largest bond energy.
Benzene and 1,3-butadiene will have relatively high energy stored in double bonds, but will be unable to match a triple bond. Propane has only single bonds and will have the lowest bond energy of these answers.
Example Question #53 : Molecular Properties
Drain cleaners are a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
The C–N bond in the original protein, before reaction with drain cleaner is __________.
stronger and longer than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
weaker and longer than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
nonpolar due to electron interaction with the lone pair on the N atom
weaker and shorter than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
stronger and shorter than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
weaker and longer than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
The C–N bond is a single bond, and the carbonyl bond is a double bond. Double bonds are stronger and shorter than single bonds.
Example Question #54 : Molecular Properties
How do the bond angles in ammonia compare to the bond angles in methane?
More information is required to answer this question.
Ammonia has smaller bond angles compared to methane.
Methane has smaller bond angles compared to ammonia.
Both compounds have the same bond angles.
Ammonia has smaller bond angles compared to methane.
Both ammonia and methane display sp3 hybridization, however, methane is surrounded by four hydrogens, while nitrogen is surrounded by three hydrogens and a lone electron pair. Lone electron pairs in a molecule require more room compared to bonding atom pairs, as they generate more electron repulsion. As a result, the lone pair in ammonia will make the bond angles in ammonia smaller than the bond angles in the methane molecule.
*Extra information: the bond angles in methane are 109.5o, while ammonia has bond angles of 107o.
Example Question #153 : Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry, And Metabolism
Which of the following molecules would have a trigonal pyramidal molecular structure?
Recall that electronic structure refers to the geometry of the atoms and lone pairs around the central atom, while the molecular structure refers strictly to the geometry of the atoms of the molecule. , , and all adopt a tetrahedral electronic geometry; however, when considering just the atoms, only NH3 has a trigonal pyramidal geometry. is trigonal planar, while is linear.
Example Question #55 : Molecular Properties
What is the molecular geometry around the carbonyl carbon in acetic acid?
Tetrahedral
Trigonal pyramidal
Trigonal planar
Bent
Trigonal planar
Acetic acid has the formula . This compound is common enough that the IUPAC name will rarely be given, and you will need to recognize it by common name alone.
The carbonyl carbon exhibits hybridization, and has no lone electron pairs. There are three atoms bonded around the carbon. In order for the atoms to be farthest away from one another, they will all orient themselves at angles within the same plane. This results in a trigonal planar geometry.
An atom with four bonds and no lone pairs will show tetrahedral geometry. An atom with two bonds and one lone pair will be bent. Trigonal pyramidal geometry results from three bonded atoms and one lone pair.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources