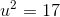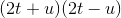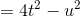All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #185 : Algebraic Concepts
Evaluate 

Example Question #1 : How To Divide Variables
The ratio of 10 to 14 is closest to what value?
0.71
0.24
0.57
0.04
0.71
Another way to express ratios is through division. 10 divided by 14 is approximate 0.71.
Example Question #2 : How To Divide Variables
If 


A quotient is the result of division. If 



Example Question #3 : How To Divide Variables

(A)
(B)
(A) and (B) are equal
It is impossible to tell which is greater from the information given
(B) is greater
(A) is greater
(B) is greater
Since the quotient of negative numbers is positive, both results will be positive.
We can rewrite both of these as products of positive numbers, as follows:


making (B) greater.
Example Question #4 : How To Divide Variables

(A)
(B)
(A) is greater
(A) and (B) are equal
(B) is greater
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) is greater
Since the quotient of negative numbers is positive, both results will be positive.
We can rewrite both of these as quotients of positive numbers, as follows:
Since the expressions have the same dividend and the second has the greater divisor, the first has the greater quotient.
Therefore, (A) is greater.
Example Question #5 : How To Divide Variables
Let 
(A)
(B)
(B) is greater
(A) is greater
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) and (B) are equal
(B) is greater
The quotient of two negative numbers is positive. The expressions can be rewritten as follows:
Both expressions have the same dividend; the second has the lesser divisor so it has the greater quotient. This makes (B) greater.
Example Question #6 : How To Divide Variables
When evaluating the expression

assuming you know the values of all five variables, what is the second operation that must be performed?
Squaring
Subtraction
Multiplication
Addition
Division
Subtraction
In the order of operations, any expression within parentheses must be performed first. Between the parentheses, there are two operations, an exponentiation (squaring), and a subtraction. By the order of operations, the exponentiation is performed first; the subtraction is performed second, making this the correct response.
Example Question #3 : How To Divide Variables

Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The reciprocal of
(b) The reciprocal of
(b) is the greater quantity
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(a) and (b) are equal
(a) is the greater quantity
(b) is the greater quantity
Since 


by the Multiplication Property of Inequality,
That is, the reciprocal of 

Example Question #25 : Variables


Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The reciprocal of
(b) The reciprocal of
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(b) is the greater quantity
(a) is the greater quantity
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
We show that the given information is insufficient by examining two cases.
Case 1:
The reciprocal of 


Also, 


Case 2: 
The reciprocal of 

Also, 



Example Question #1 : How To Subtract Variables
Simplify:
All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources