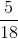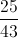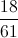All Common Core: 7th Grade Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #531 : Data Analysis And Probability
Billy's mom baked a pizza with eight slices. Half the slices have pepperoni only. Two of the slices have both pepperoni and onions. One slice has onions only. One slice has only cheese.
If Billy is allergic to pepperoni, and takes a slice of pizza with his eyes blindfolded, what is the percentage chance that he will select a piece he is not allergic to?


The pizza that Billy's mom baked was composed of these types of slices:
Half the slices have pepperoni only. Two of the slices have both pepperoni and onoins. One slice has onions only. One slice has only cheese.
Therefore,




Billy could eat either the onion only slice, or the cheese only slice. This means that out of 

Given that 

Example Question #802 : Grade 7
Two fair dice are thrown. What is the probability that the difference of the numbers that show on the dice will be exactly 
The following rolls result in the difference of the dice being 

These are 

Example Question #532 : Data Analysis And Probability
Two fair six-sided dice are thrown. What is the probability that the product of the two numbers rolled is between 

The rolls that yield a product between 

Therefore there are 


Example Question #31 : Develop And Compare Probability Models And Find Probabilities Of Events: Ccss.Math.Content.7.Sp.C.7
A loaded coin is tossed 

The probability of an event based on observation (empirical probability) can be calculated by dividing the number of times the event occurs by the number of trials total. Since there were 


The probability of tails is therefore given by the number of tails divided by the total number of trials. Both terms are divisible by 
Example Question #801 : Grade 7
A pair of fair six-sided dice are thrown, and the sum of the numbers facing upward is noted. What is the probability that a sum of 8 or 9 will be thrown?
There are 

There are 9 ways out of 36 to roll a sum of 8 or 9, making the probability of this outcome 
Example Question #99 : Statistics & Probability
What is the probability of drawing a 10 from a deck of cards?
To find the probability of an event, we will use the following formula:
So, if we look at the event of drawing a 10 from a deck of cards, we can determine the following:
because there are 4 ways we can draw a 10:
- 10 of hearts
- 10 of diamonds
- 10 of clubs
- 10 of spades
because there are 52 total cards to choose from.
Knowing all of this, we can substitute into the formula. We get
Now, we simplify.
Therefore, the probability of drawing a 10 from a deck of cards is 
Example Question #100 : Statistics & Probability
In a dice game, what is the probability of rolling an even number on one roll of a six-sided die?
To find the probability of an event, we will use the following formula:
So, if we look at the event of rolling an even number on a dice, we can determine the following:
because there are 3 ways we can roll an even number on a dice:
- 2
- 4
- 6
because there are 6 possible numbers we can roll:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Knowing all of this, we can substitute into the formula. We get
Now, we simplify.
Therefore, the probability of rolling an even number on a dice is 
Example Question #33 : Develop And Compare Probability Models And Find Probabilities Of Events: Ccss.Math.Content.7.Sp.C.7
Find the probability of drawing a 2 from a deck of cards.
To find the probability of an event, we use the following formula:
Now, we are asked to find the probability of drawing a 2 from a deck of cards. Given that event, we can determine
because there are 4 ways to draw a 2 from a deck of cards:
- 2 of hearts
- 2 of diamonds
- 2 of clubs
- 2 of spades
Now, we can determine the total number of possible outcomes
because there are 52 different cards to choose from.
Knowing this, we can substitute into the formula.
Now, we can simplify.
Therefore, the probability of drawing a 2 from a deck of cards is 
Example Question #34 : Develop And Compare Probability Models And Find Probabilities Of Events: Ccss.Math.Content.7.Sp.C.7
Find the probability of drawing an Ace of spades from a deck of cards.
To find the probability of an event, we use the following formula:
Now, we are asked to find the probability of drawing an Ace of spades from a deck of cards. Given that event, we can determine
because there is only 1 Ace of spades in a deck of cards.
Now, we can determine the total number of possible outcomes
because there are 52 different cards to choose from.
Knowing this, we can substitute into the formula.
Therefore, the probability of drawing an Ace of spades from a deck of cards is 
Example Question #35 : Develop And Compare Probability Models And Find Probabilities Of Events: Ccss.Math.Content.7.Sp.C.7
Find the probability of drawing a King from a deck of cards.
To find the probability of an event, we will use the following formula:
So, given the event of drawing a King from a deck of cards, we can see
because there are 4 Kings in a deck of cards:
- King of Hearts
- King of Diamonds
- King of Clubs
- King of Spades
Now, we will look at total outcomes. We get
because there are 52 cards in a deck (in other words 52 different possibilities when drawing a card).
Knowing this, we can substitute into the formula. We get
Now, we simplify.
Therefore, the probability of drawing a King from a deck of cards is 
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All Common Core: 7th Grade Math Resources