All Calculus 2 Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Power Series
What is the radius of convergence for the following power series?
No radius of convergence.
With every power series, you must first start by using the ratio test.
The 

Using the ratio test you get

Canceling things out and taking the 

Because the ratio test states that the series can only converge if the absolute value of x is less than or equal to 1, this means that x is between -1 and 1. And so the radius of convergence is 1.
Example Question #75 : Taylor And Maclaurin Series
Determine the Taylor Series of 

Recall that a Taylor Series approximation at 

In our case,
So, our final summation will look like

Example Question #76 : Taylor And Maclaurin Series
Find the Maclaurin Series for the function 
We can use the common Maclaurin Series expansion,
and modify it to fit our current function 
First, we substitute 


The remaining task is to get the 

Doing so, we obtain,

Thus our Maclaurin Series for 

Note: One could also try to use the Maclaurin Series formula 


There are a few others that are useful, but these are the most commonly used in classroom and exam settings.
Example Question #7 : Power Series
Find a convergent power series representation for the function. Base the derivation of the power series on a convergent geometric series.
To find a convergent power series representation of the function we can use the following theorem for an infinite geometric series that converges to a finite value:
_________________________________________________________


________________________________________________________
First factor the function to so that one of the factors is comparable to the form 
Now we can use the theorem to write the 



The series we will derive a power series that will converge to the factor 


Using the theorem for a convergent infinite series, valid in this case for 
Now simply bring back the other factor, 
To find where the power series we've obtained converges, we simply have to apply the condition for the convergence of the geometric series 



This is equivalent to the interval 


Example Question #321 : Series In Calculus
Find a series representation of

This is an indefinite integral so we can eliminate answers without the +C.
First, we need to find a power series representation for sin(x), which is

We then substitute in 




Example Question #321 : Series In Calculus
Let 


What is the Lagrange error of the polynomial approximation to 
The fifth degree Taylor polynomial approximating 

The Lagrange error is the absolute value of the next term in the sequence, which is equal to .
We need only evaluate this at and thus we obtain
Example Question #1 : Abstract Algebra
Which of the following series does not converge?
We can show that the series 
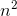

Alternatively, it's clear that 



The other series will converge by alternating series test, ratio test, geometric series, and comparison tests.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All Calculus 2 Resources













































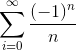



![L = \lim_{n ->\infty } \frac{a_{n+1}}{a_{n}} = \lim_{n ->\infty } \left[\left(\frac{(n+1)!}{(n+1)^2 cos (n+1)} \div \frac{n!}{n^2 cos (n) }\right)\right]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/343419/gif.latex)




