All Basic Geometry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #53 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A Right Triangle
Find the perimeter.

How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle?
There are three primary methods used to find the perimeter of a right triangle.
- When side lengths are given, add them together.
- Solve for a missing side using the Pythagorean theorem.
- If we know side-angle-side information, solve for the missing side using the Law of Cosines.
Method 1:
This method will show you how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle when all sides lengths are known. Consider the following figure:

If we know the lengths of sides 


Method 2:
In right triangles, we can calculate the perimeter of a triangle when we are provided only two sides. We can do this by using the Pythagorean theorem. Let's first discuss right triangles in a general sense. A right triangle is a triangle that has one 





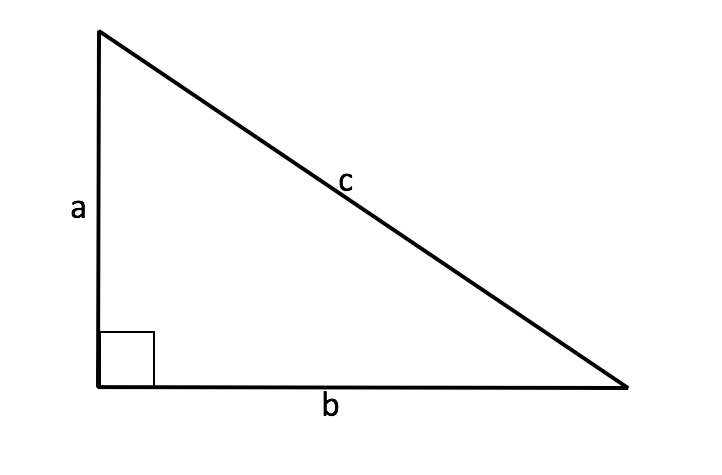
If a triangle appears in this format, then we can use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for any missing side. This formula is written in the following manner:
We can rearrange it in a number of ways to solve for each of the sides of the triangle. Let's rearrange it to solve for the hypotenuse, 
Rearrange and take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Now, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for one of the legs, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Last, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for the adjacent leg, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
It is important to note that we can only use the following formulas to solve for the missing side of a right triangle when two other sides are known:
After we find the missing side, we can use the perimeter formula to calculate the triangle's perimeter.
Method 3:
This method is the most complicated method and can only be used when we know two side lengths of a triangle as well as the measure of the angle that is between them. When we know side-angle-side (SAS) information, we can use the Law of Cosines to find the missing side. In order for this formula to accurately calculate the missing side we need to label the triangle in the following manner:

When the triangle is labeled in this way each side directly corresponds to the angle directly opposite of it. If we label our triangle carefully, then we can use the following formulas to find missing sides in any triangle given SAS information:
After, we calculate the right side of the equation, we need to take the square root of both sides in order to obtain the final side length of the missing side. Last, we need to use the perimeter formula to obtain the distance of the side lengths of the polygon.
Solution:
Now, that we have discussed the three methods used to calculate the perimeter of a triangle, we can use this information to solve the problem.
Recall how to find the perimeter of a triangle:
The given triangle has 
Recall the Pythagorean theorem:

Since we are finding the length of the hypotenuse, 
Plug in the values of 

Now, plug in all three values into the equation to find the perimeter. Use a calculator and round to 
Example Question #54 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A Right Triangle
Find the perimeter.

How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle?
There are three primary methods used to find the perimeter of a right triangle.
- When side lengths are given, add them together.
- Solve for a missing side using the Pythagorean theorem.
- If we know side-angle-side information, solve for the missing side using the Law of Cosines.
Method 1:
This method will show you how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle when all sides lengths are known. Consider the following figure:

If we know the lengths of sides 


Method 2:
In right triangles, we can calculate the perimeter of a triangle when we are provided only two sides. We can do this by using the Pythagorean theorem. Let's first discuss right triangles in a general sense. A right triangle is a triangle that has one 






If a triangle appears in this format, then we can use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for any missing side. This formula is written in the following manner:
We can rearrange it in a number of ways to solve for each of the sides of the triangle. Let's rearrange it to solve for the hypotenuse, 
Rearrange and take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Now, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for one of the legs, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Last, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for the adjacent leg, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
It is important to note that we can only use the following formulas to solve for the missing side of a right triangle when two other sides are known:
After we find the missing side, we can use the perimeter formula to calculate the triangle's perimeter.
Method 3:
This method is the most complicated method and can only be used when we know two side lengths of a triangle as well as the measure of the angle that is between them. When we know side-angle-side (SAS) information, we can use the Law of Cosines to find the missing side. In order for this formula to accurately calculate the missing side we need to label the triangle in the following manner:

When the triangle is labeled in this way each side directly corresponds to the angle directly opposite of it. If we label our triangle carefully, then we can use the following formulas to find missing sides in any triangle given SAS information:
After, we calculate the right side of the equation, we need to take the square root of both sides in order to obtain the final side length of the missing side. Last, we need to use the perimeter formula to obtain the distance of the side lengths of the polygon.
Solution:
Now, that we have discussed the three methods used to calculate the perimeter of a triangle, we can use this information to solve the problem.
Recall how to find the perimeter of a triangle:
The given triangle has 
Recall the Pythagorean theorem:

Since we are finding the length of the hypotenuse, 
Plug in the values of 

Now, plug in all three values into the equation to find the perimeter. Use a calculator and round to 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle
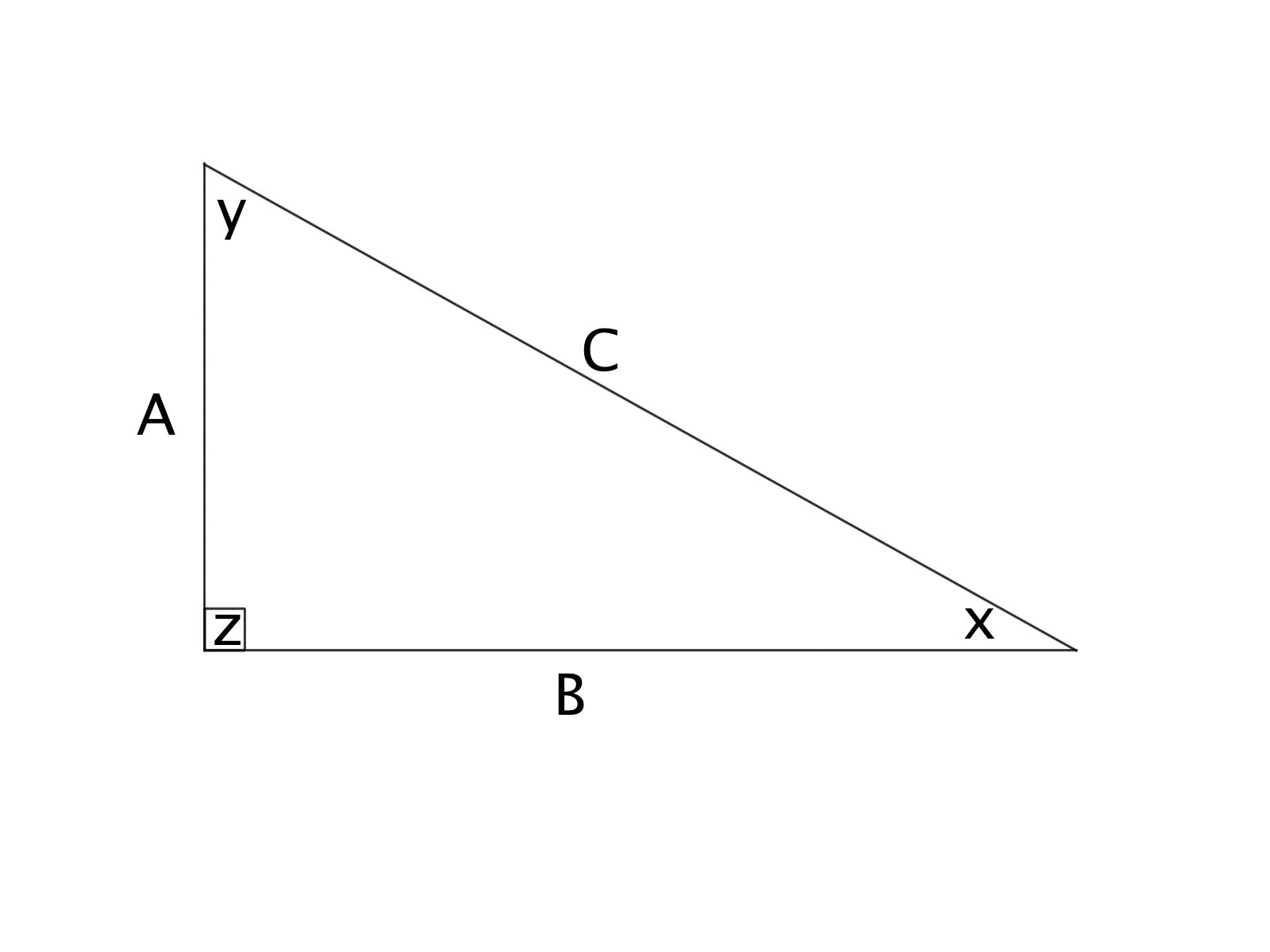
Given:
A = 3 cm
B = 4 cm
What is the area of the right triangle ABC?
7 square centimeters
6 square centimeters
5 square centimeters
12 square centimeters
13 square centimeters
6 square centimeters
The area of a triangle is given by the equation:
Since the base leg of the given triangle is 4 cm, while the height is 3 cm, this gives:
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle

Given:
A = 4 cm
B = 6 cm
What is the area of the right triangle ABC?
8 square centimeters
12 square centimeters
11 square centimeters
10 square centimeters
24 square centimeters
12 square centimeters
The area of a triangle is given by the equation:
Since the base leg of the given triangle is 4 cm, while the height is 3 cm, this gives:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle

Given:
A = 3 cm
B = 7 cm
What is the area of the triangle?
10 square centimeters
8.3 square centimeters
7 square centimeters
10.5 square centimeters
7.6 square centimeters
10.5 square centimeters
The area of a triangle is given by the equation:
Since the base leg of the given triangle is 4 cm, while the height is 3 cm, this gives:
Example Question #4 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle

Given that:
A = 6 cm
B = 10 cm
What is the area of the right trianlge ABC?
16 square centimeters
35 square centimeters
90 square centimeters
60 square centimeters
30 square centimeters
30 square centimeters
The area of a triangle is given by the equation:
Since the base leg of the given triangle is 4 cm, while the height is 3 cm, this gives:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle

Given that:
A = 3 cm
B = 4 cm
C = 5 cm
What is the area of the right triangle ABC?
6.5 square centimeters
12 square centimeters
6 square centimeters
10 square centimeters
7 square centimeters
6 square centimeters
The area of a triangle is given by the equation:
Since the base leg of the given triangle is 4 cm, while the height is 3 cm, this gives:
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle

Given that:
A = 10 cm
B = 20 cm
What is the area of the right triangle ABC?
50 square centimeters
100 square centimeters
70 square centimeters
120 square centimeters
30 square centimeters
100 square centimeters
The area of a triangle is given by the equation:
Since the base leg of the given triangle is 4 cm, while the height is 3 cm, this gives:
Example Question #7 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle
The length of the legs of the triangle below (not to scale) are as follows:



What is the area of the triangle?






The formula for the area of a triangle is
where 

For the triangle shown, side 

Therefore, the area is equal to
or, based on the units given, 42 square centimeters
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle
An equilateral triangle has a side of 
What is the area of the triangle?
An equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. The area of a triangle is given by 


The equilateral triangle can be broken into two 



Using the Pythagorean Theorem we get 

All Basic Geometry Resources































































