All AP Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #21 : P H And Poh Of Strong Acids And Bases
Which of the following is a strong acid?
Lactic acid
Formic acid
Nitric acid
Hydroflouric acid
Acetic acid
Nitric acid
This question is simply testing your memorization of strong and weak acids. Of the list, you should recognize that nitric acid is the only strong acid, and the rest of the choices are weak.
Example Question #1 : Using Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
Which of the following is what determines the strength of an acid?
The Ka
How many bonds the central atom makes
Its physical state
The Kb
Electronegativity values
The Ka
The Ka is the acid dissociation constant, and thus it is what determines how strong the acid is. Stronger acids dissociate to a greater extent and produce lower pH values.
Example Question #1 : Using Base Dissociation Constant (Kb)
A 1M solution of a monoprotic acid has a pH of 4.6. What is the 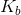
In order to find the base dissociation constant for the conjugate base, we can start by finding the acid dissociation constant for the acid. Since a 1M solution of the acid has a pH of 4.6, we can find the proton concentration of the solution.
Since the acid is monoprotic, we can set the following equilibrium expression equal to its acid dissociation constant.
We can see that, since the acid is monoprotic, the concntration of protons will be equal to the concentration of the acid anion. The final concentration of the acid molecule will be equal to the initial concentration, minus the amount of protons formed. Using these values, we can solve for the equilibrium constant for the acid.
Now that we have the acid dissociation constant, we can find the conjugate base's dissociation constant by setting the product of the two values equal to the autoionization of water.
Example Question #981 : Ap Chemistry
Would H2SO4 or HNO3 produce a more acidic solution?
H2SO4 since it has a lower pKa
H2SO4 since it has a higher pKa
HNO3 since it has a higher pKa
HNO3 since it has a lower pKa
H2SO4 since it has a lower pKa
Both are strong acids, but H2SO4 is bivalent, realeasing 2 protons for each molecule dissolved in solution. Further, a more acidic solution would have a lower pKa.
Example Question #22 : P H And Poh Of Strong Acids And Bases
Which of the following species will not be present in an aqueous solution of 
All of these will be present in the solution
The hydroxide ion (OH–) is a strong base and therefore would not be present in an acidic solution. Protons, the hydronium ion, and water will all be present in relatively large amounts within the solution.
Example Question #182 : Reactions And Equilibrium
Which of the following anions is the strongest base?
Weaker acids dissociate less in water and therefore, reverse reaction is favored in




Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All AP Chemistry Resources



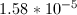

![pH=-\log[H^+]\rightarrow [H^+]=10^{-pH}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/121717/gif.latex)
![\small [H^{+}] = 10^{-4.6} = 2.51*10^{-5}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94835/gif.latex)
![\small K_{a} = \frac{[H^{+}][A^{-}]}{[HA]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/121718/gif.latex)
![K_a= \frac{[2.51*10^{-5}]^{2}}{[1-2.51*10^{-5}]} = 6.31*10^{-10}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94836/gif.latex)