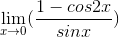All AP Calculus AB Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Derivatives
Define 
Give the interval(s) on which 

<0)
We need to find the values of 
&space;=&space;3x%5E%7B2%7D&space;-18x+24&space;<0)
These are the boundary points, so the intervals we need to check are:


We check each interval by substituting an arbitrary value from each for 
Choose

Choose

Choose

The answer is that 

Example Question #2 : Derivatives
Define &space;=&space;x%5E%7B3%7D&space;-&space;%5Cfrac%7B21%7D%7B2%7D&space;x%5E%7B2%7D&space;+30x&space;-6)
Give the interval(s) on which 

>0)
We need to find the values of 

These are the boundary points, so the intervals we need to check are:


We check each interval by substituting an arbitrary value from each for 
Choose

Choose

Choose

The answer is that 
Example Question #1 : Finding Regions Of Increasing And Decreasing Value
At what point does 
It does not shift from increasing to decreasing
To find out where the graph shifts from increasing to decreasing, we need to look at the first derivative.
To find the first derivative, we can use the power rule. We lower the exponent on all the variables by one and multiply by the original variable.
We're going to treat 

Notice that 
If we were to graph 
Example Question #2 : Finding Regions Of Increasing And Decreasing Value
At what value of 

It does not shift from decreasing to increasing
To find out when the function shifts from decreasing to increasing, we look at the first derivative.
To find the first derivative, we can use the power rule. We lower the exponent on all the variables by one and multiply by the original variable.
Anything to the zero power is one.
From here, we want to know if there is a point at which graph changes from negative to positive. Plug in zero for y and solve for x.
This is the point where the graph shifts from decreasing to increasing.
Example Question #1 : Derivative Interpreted As An Instantaneous Rate Of Change
Evaluate the following limit:
When 



Example Question #1 : Derivative Interpreted As An Instantaneous Rate Of Change
Find the instantaneous rate of change for the function,
at the point 
Find the instantaneous rate of change for the function,
at the point 
1) First compute the derivative of the function, since this will give us the instantaneous rate of change of the function as a function of 
2) Now evaluate the derivative at the value 
Therefore, 


Example Question #1 : Derivative Interpreted As An Instantaneous Rate Of Change
A particle is traveling in a straight line along the x-axis with position function 

To find the instantaneous rate of change of the particle at time 



And

Hence the instantaneous rate of change in position (or just 'velocity') of the particle at 

Example Question #2 : Derivative Interpreted As An Instantaneous Rate Of Change
Find the function values and as well as the instantaneous rate of change for the function 
Find the instantaneous rate of change for the function 
Evaluate the function at each value of
The instantaneous rate of change at any point 
Apply the product rule:
Therefore,
Now evaluate the derivative for each given value of 
Therefore, the instantaneous rate of change of the function 

Example Question #2 : Derivative Interpreted As An Instantaneous Rate Of Change
Given that v(t) is the velocity of a particle, find the particle's acceleration when t=3.
Not enough information provided
Given that v(t) is the velocity of a particle, find the particle's acceleration when t=3.
We are given velocity and asked to find acceleration. Our first step should be to find the derivative.
We can use our standard power rule for our 1st and 3rd terms, but we need to remember something else for our second term. Namely, that the derivative of 
With that in mind, let;s find v'(t)
Now, for the final push, we need to find the acceleration when t=3. We do this by plugging in 3 for t and simplifying.
So, our answer is 123.5
Example Question #4 : Derivative Interpreted As An Instantaneous Rate Of Change
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All AP Calculus AB Resources




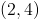
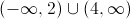

&space;=&space;3%5Ccdot&space;x%5E%7B3-1%7D&space;-2%5Ccdot&space;9x%5E%7B2-1%7D+24+0)