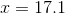All Algebra II Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #94 : Factorials
Try without a calculator.
Give the value of 
The inequality has no solution.
Given a nonnegative integer 



Multiplying by 8, we find that
Multiplying by 9, we find that
Therefore,
Since only integers may have factorial values, it follows that the only value of 

Example Question #95 : Factorials
Try without a calculator:

None of these



and

the correct response.
Example Question #2901 : Algebra Ii
Try without a calculator:
Which is true about 

Cannot be determined

Example Question #97 : Factorials
Try without a calculator:
Calculate:
Cannot be determined



Therefore,
Since

it follows that 720 is the correct response.
Example Question #1 : Understanding Logarithms
Solve for 
The first thing we notice about this problem is that 
The question is, which base should we choose for the log? We should use the natural log (log base e) because the right-hand side of the equation already has e as a base of an exponent. As you will see, things cancel out more nicely this way.
Take the natural log of both sides:
Rewrite the right-hand side of the equation using the product rule for logs:
Now rewrite the whole equation after bringing down those exponents.


Now we just divide by 

Example Question #1 : Natural Log
Rewrite as a single logarithmic expression:
Using the properties of logarithms


we simplify as follows:
Example Question #2 : Natural Log
Which of the following expressions is equal to the expression 
None of the other responses is correct.
By the reverse-FOIL method, we factor the polynomial as follows:
Therefore, we can use the property
as follows:
Example Question #2 : Understanding Logarithms
Solve 
The original equation is:
Subtract 
Divde both sides by 
Take the natural logarithm of both sides:
Divde both sides by 
Example Question #3 : Natural Log
What are the domain and the range of the function 
Domain = all positive numbers
Range = all non-negative numbers
Domain = all non-negative numbers
Range = all positive numbers
Domain = all positive numbers
Range = all positive numbers
Domain = all positive real numbers
Range = all real numbers
Domain = all real numbers
Range = all real numbers
Domain = all positive real numbers
Range = all real numbers
Remember that 

It's not possible to raise 
, for example, is just
, which is a ratio of two positive numbers, and therefore positive.
More than that, it's also not possible to obtain 0 by raising 
So the domain is strictly positive. It excludes negative numbers and 0.
What about the range? To what possible values are we allowed to exponentiate 
Well, we just saw that 


And we can obviously raise it to positive powers. So the range is all real numbers. It includes negative numbers, 0, and positive numbers.
Example Question #3 : Understanding Logarithms
Solve for 

If necessary, round to the nearest tenth.
No solution
Give both sides the same base, using e:

Because e and ln cancel each other out, 
Solve for x and round to the nearest tenth:
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All Algebra II Resources