All ACT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #2991 : Act Math

The above circle has a radius of 



We can solve for the length of the chord by drawing a line the bisects the angle and the chord, shown below as 

In this circle, we can see the triangle 




The length of the entire chord is twice the length of 

Example Question #5 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine

What is 
Recall that the sine of an angle is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse of that triangle. Thus, for this triangle, we can say:
Solving for 

Example Question #6 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine
A man has set up a ground-level sensor to look from the ground to the top of a 

Begin by drawing out this scenario using a little right triangle:

Note importantly: We are looking for 
Using your calculator, solve for 
This is 
Thus, rounded, your answer is 

Example Question #7 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine
Below is right triangle 




To find the sine of an angle, remember the mnemonic SOH-CAH-TOA.
This means that

We are asked to find the 



Example Question #8 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine
In a given right triangle 




In right triangles, SOHCAHTOA tells us that 




Thus, 
Example Question #9 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine
In a given right triangle 




In right triangles, SOHCAHTOA tells us that 




Thus, 
Example Question #10 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine
In a given right triangle 




In right triangles, SOHCAHTOA tells us that 



Thus, 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Sine Of An Angle

What is the sine of 
Sine can be found using the SOH CAH TOA method. For sine we do 
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Sine Of An Angle
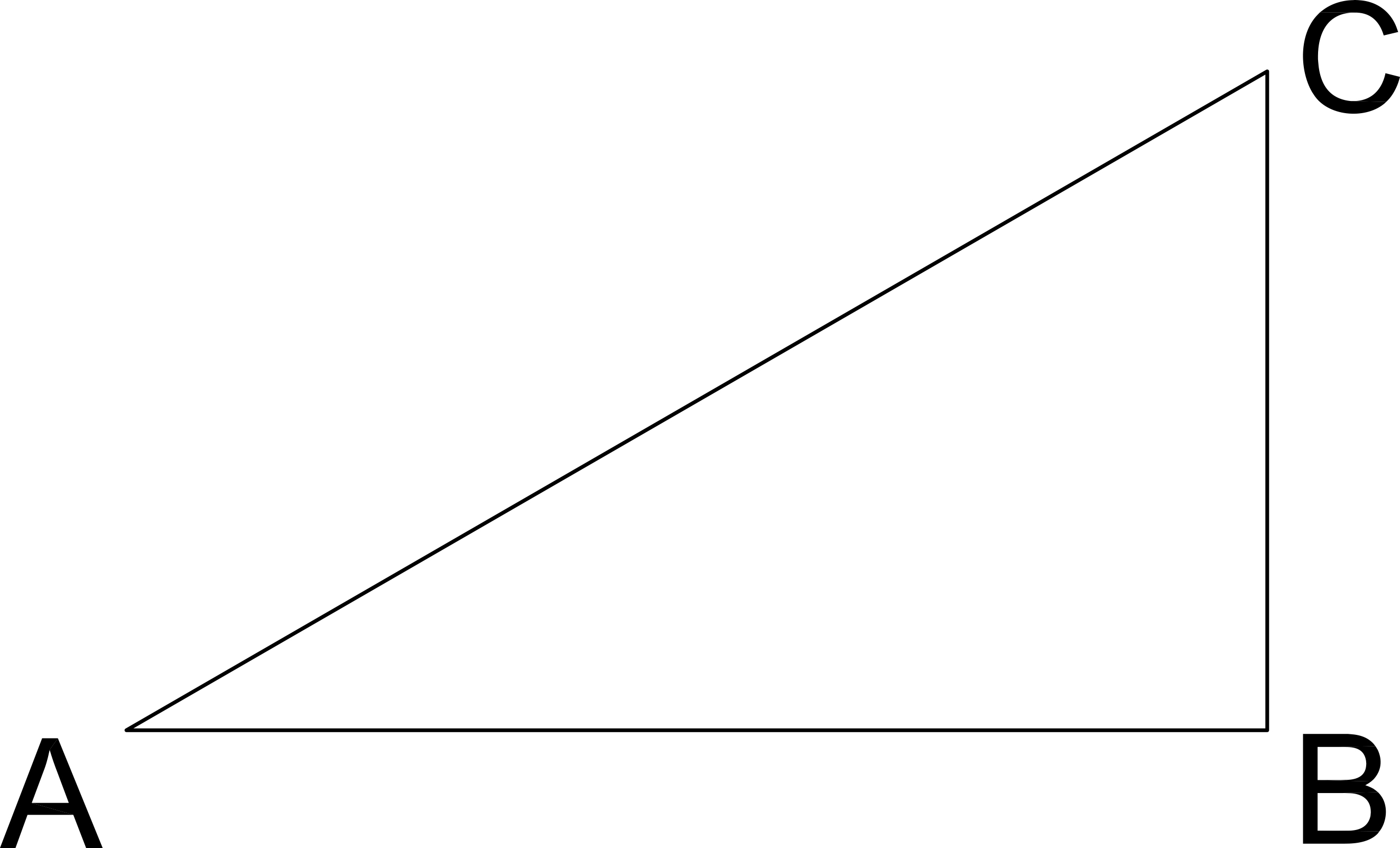
See right triangle ABC. If the length AB is 8 and the length of BC is 6, what is the sine of angle A?
0.8
0.6
10
6
1
0.6
Sine A = Opposite / Hypotenuse = BC / AC
To find AC, use Pythagorean Theorum
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
82 + 62 = AC2
64 + 36 = AC2
100 = AC2
AC = 10
Sine A = BC / AC = 6 / 10 = 0.6
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Sine Of An Angle
Solve for 
Q = π or does not exist 2
Q = π or 2π
Q = 3π or does not exist 2
Q = π or 3π 2 2
Q = 3π or does not exist 2
Substitute x = sinQ and solve the new equation x2 + 3x = –2 by factoring. Be sure to change variables back to Q. As a result, sinQ = –1 or sinQ = –2. This function is bounded between –1 and 1 so sinQ can never be –2 and sinQ is –1 only at 3π/2 or 270 °.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ACT Math Resources






























































