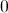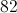All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #45 : Algebra
The first step to solving is to use the Order of Operations.
The absolute value of a real number x is the non-negative value of x without regard to its sign. The absolute value of a number is the distance of that number from the point of origin or zero on a number line.
Example Question #42 : Algebra
and
and
and
and
and
To solve this Absolute Value inequality, remove the Absolute Value bars and create two linear inequalities.
Then, using the Order of Operations and the method for solving multi-step equations solve.
First inequality:
Second inequality:
The solution to consists of the two intervals and . This pair of inequalities is the solution.
Example Question #43 : Algebra
and
and
and
and
and
To solve this Absolute Value inequality, remove the Absolute Value bars and create two linear inequalities.
and
Then solve each of the inequalities.
First inequality:
Second inequality:
The solution to 
Example Question #21 : How To Find Absolute Value
and
and
and
and
and
To solve this Absolute value inequality, remove the absolute value bars and create two linear inequalities and solve.
The solution to consists of the two intervals and .
This pair of inequalities is the solution.
Example Question #47 : Algebra
Step One: Order of Operations
The absolute value of is However, because there is a negative sign outside the Absolute value bars, you would multiply the by to get the solution.
The correct answer is
Example Question #21 : How To Find Absolute Value
Micah is seeking new employment. The salary that he desires must be $4,000 per month with a tolerance of $600. Which absolute value inequality can be used to assess the salary which will be tolerable?
is the correct solution.
This absolute value inequality states that the difference between the salary of $4,000 must be less than or equal to $600 to be tolerable.
Example Question #22 : Absolute Value
In order to ride the roller coaster at the local amusement park, children must be tall with a tolerance of Which of the following absolute value inequalities can be used to assess which heights will be tolerable?
is the correct solution.
This Absolute Value inequality states that the difference between the children's height and must be less than or equal to .
Example Question #23 : Absolute Value
Using compare the following absolute value.
__________
The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero. The absolute value of a negative integer is a positive integer. The distance from zero to on a number line is , so
The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero. The absolute value of a negative integer is a positive integer. The distance from 0 to on a number line is . Therefore:
Therefore
because
Example Question #182 : Integers
Evaluate the expression if and .
To solve, we replace each variable with the given value.
Simplify. Remember that terms inside of the absolute value are always positive.
Example Question #22 : How To Find Absolute Value
Evaluate:
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources