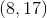All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #291 : Coordinate Geometry
What coordinate point is the black circle on?

To find the location on a coordinate plane we first look at the 



The black circle is over 



Example Question #292 : Coordinate Geometry
What coordinate point is the orange triangle on?

To find the location on a coordinate plane we first look at the 



The orange triangle is over 



Example Question #293 : Coordinate Geometry
What coordinate point is the green triangle on?

To find the location on a coordinate plane we first look at the 



The green triangle is over 



Example Question #21 : Understand A Coordinate System: Ccss.Math.Content.5.G.A.1
What coordinate point is the blue circle on?

To find the location on a coordinate plane we first look at the 



The blue circle is over 



Example Question #22 : Understand A Coordinate System: Ccss.Math.Content.5.G.A.1
What coordinate point is the red circle on?

To find the location on a coordinate plane we first look at the 



The red circle is over 



Example Question #294 : Coordinate Geometry
Starting at the coordinate point shown below, if you move up 


The starting point is at 


Moving up the 

Moving down the 

Because we are moving up 





Example Question #295 : Coordinate Geometry
Starting at the coordinate point shown below, if you move up 


The starting point is at 


Moving up the 

Moving down the 

Because we are moving up 





Example Question #296 : Coordinate Geometry
Starting at the coordinate point shown below, if you move up 


The starting point is at 


Moving up the 

Moving down the 

Because we are moving up 





Example Question #297 : Coordinate Geometry
Starting at the coordinate point shown below, if you move up 


The starting point is at 


Moving up the 

Moving down the 

Because we are moving up 





Example Question #298 : Coordinate Geometry
Starting at the coordinate point shown below, if you move up 


The starting point is at 


Moving up the 

Moving down the 

Because we are moving up 





Certified Tutor
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources