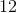All SAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #92 : Plane Geometry

If Bailey paints the wall shaped like above and uses one bucket per 5 square units, how many buckets does Bailey need?
To solve, we will need to find the area of the wall. We can do this by finding the areas of each section and adding them together. Break the area into a rectange and two triangles.

The area of the rectangle will be equal to the base times the height. The area of each triangle will be one half its given base times its height.
For the rectangle, the base is 12 and the height is 4 (both given in the figure).
The triangle to the right has a given base of 6, but we need to solve for its height. The height will be equal to the difference between the total height (6) and the height of the rectangle (4).
We now have the base and height of the triangle to the right, allowing us to calculate its area.
Now we need to solve the triangle to the left. We solved for its height (2), but we still need to solve for its base. The total base of the rectangle is 12. Subtract the base of the right-side triangle (6) and the small segment at the top of the rectangle (3) from this total length to solve for the base of the left triangle.
The left-side triangle has a base of 3 and a height of 2, allowing us to calculate its area.
Add together the two triangles and the rectangle to find the total area.
We know that each bucket of paint will cover 5 square units, and we have 57 square units total. Divide to find how many buckets are required.
We will need 11 full buckets and part of a twelfth bucket to cover the wall, meaning that we will need 12 buckets total.
Example Question #93 : Plane Geometry
A square is inscribed within a circle with a radius 
First, find the area of the circle.
Next, find the length of 1 side of the square using the Pythagorean Theorem. Two radii from the center of the circle to adjacent corners of the square will create a right angle at the center of the circle. The radii will be the legs of the triangle and the side of the square will be the hypotenuse.
Find the area of the square.
Subtract the area of the square from the area of the circle.
Certified Tutor
All SAT Math Resources