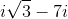All SAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Complex Numbers
From 
The complex conjugate of a complex number 



Example Question #2 : Complex Numbers
From 
The complex conjugate of a complex number 



Example Question #1 : Complex Numbers
From 
The complex conjugate of a complex number 



Example Question #1 : Complex Numbers
Simplify:
Rewrite 
Example Question #1 : Complex Numbers
Add 
The complex conjugate of a complex number 




the correct response.
Example Question #2 : Complex Numbers
Add 
The complex conjugate of a complex number 



Example Question #4 : Complex Numbers
An arithmetic sequence begins as follows:
Give the next term of the sequence
The common difference 
Add this to the second term to obtain the desired third term:

Example Question #1 : Complex Numbers
Simplify:
It can be easier to line real and imaginary parts vertically to keep things organized, but in essence, combine like terms (where 'like' here means real or imaginary):
Example Question #2 : Complex Numbers
For 

The complex conjugate of a complex number 



Example Question #12 : Squaring / Square Roots / Radicals
Evaluate:
None of these
A power of 




Substituting:
Collect real and imaginary terms:
All SAT Math Resources