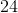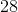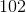All SAT II Math I Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #2 : Cones
The circumference of the base of a cone is 100; the height of the cone is equal to the diameter of the base. Give the surface area of the cone (nearest whole number).
The formula for the surface area of a cone with base of radius 


The diameter of the base is the circumference divided by 
This is also the height 
The radius is half this, or
The slant height can be found by way of the Pythagorean Theorem:
Substitute in the surface area formula:
Example Question #21 : How To Find The Surface Area Of A Cone
If a cone were unfurled into a 2-dimensional figure. The lateral area of the cone would look most like which figure?
Triangle
Circle
Rectangle
Sector of a Circle
Sector of a Circle
When creating a net image of a 3D figure - one imagines it is made of paper and is unfurled into its' 2D form. The lateral portion of the cone cone would be unfurled into the image of a Sector of a Circle. To include the full surface area of the cone a circle is included to form the base of the cone as in the figure below. The lateral area portion is the top part of the figure below.

Example Question #51 : 3 Dimensional Geometry
Find the surface area of a cube with side length of 6in.
A cube is made up of 6 identical sides. Find the area of one side and multiplying it by 6 will result in the surface area of a cube.
a is the side length, in this case 6in.
Example Question #53 : 3 Dimensional Geometry
What is the surface area of a cylinder with height 10 and radius 7?
The formula of the surface area of a cylinder is:
In this problem h is 10 and r is 7. Substituting in those values gives us:
Simplifying and combining the like terms results in:
Example Question #54 : 3 Dimensional Geometry
Figure not drawn to scale.

Find the surface area of the box above.
Surface area: 84 yd2
Surface area: 84 yd3
Surface area: 82 yd3
Surface area: 82 yd2
Surface area: 48 yd2
Surface area: 82 yd2

You can find the surface area of a box by following the equation below:
The surface area of the box is 82yd2 (remember that area measurements are square units NOT cubic units)
Example Question #55 : 3 Dimensional Geometry
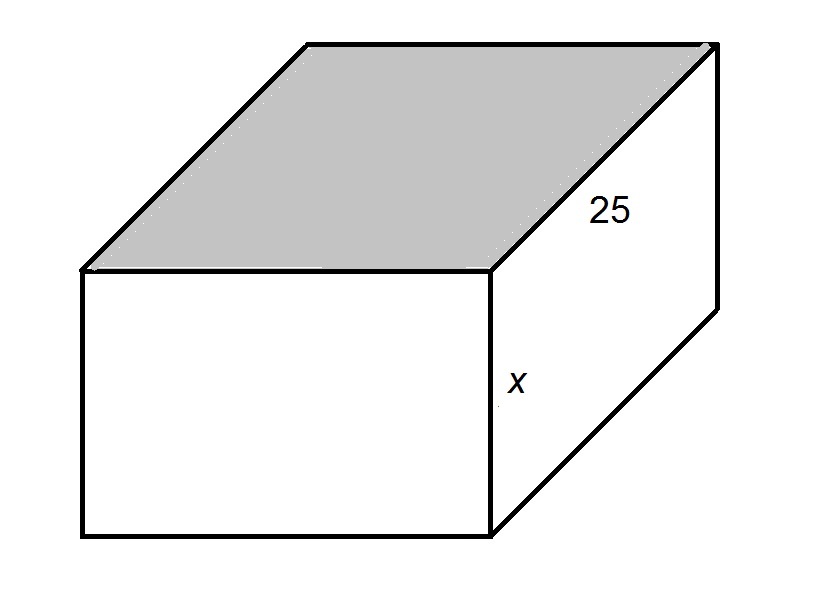
The shaded face of the provided rectangular prism is a square. If the surface area of the prism is 


Since the top face of the prism is a square, the common sidelength - and the missing dimension - is 25.
The surface area 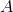




Setting

Example Question #51 : 3 Dimensional Geometry
How many vertices does a polyhedron with twenty faces and thirty edges have?
By Euler's Formula, the relationship between the number of vertices 


Set 


The polyhedron has tweve vertices.
Example Question #131 : Geometry
How many edges does a polyhedron with nine vertices and eleven faces have?
By Euler's Formula, the relationship between the number of vertices 


Set 


The polyhedron has eighteen edges.
Example Question #131 : Geometry
A rectangular prism has a height of 4 in., length of 8in., and a width of 7in. Find the volume of the prism.
To find the volume of a rectangular prism we use the equation of:
Now substituting in our values we get:
Example Question #51 : 3 Dimensional Geometry
What is the volume of a triangular prism having a base of 2, a height of 8, and second height of 14?
To find the volume of a triangular prism we use the equation
In our case our
Therefore,
All SAT II Math I Resources