All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #11 : Carbonyl Reactants
The compound below is reacted with . What is the final hybridization around the initially chiral center carbon when the reaction is complete?

The initially chiral carbon has an hybridization. Once treated with ,an oxidizing agent, the secondary alcohol in the compound is oxidized to a ketone. The central carbon is no longer a chiral center (a carbon with a double bond cannot be chiral), and the double bond (pi-bond) formed between carbon and oxygen gives the molecule an hybridization.
hybridization is formed with triple bonds, and an hybridization does not exist.
Example Question #582 : Organic Chemistry

What is the product of the reaction when the given molecule is introduced to an acidic solution?
4-bromo-2-hexene
None of these
2-bromo-4-hexene
2-bromo-4-hexanol
3-bromo-5-hexanol
4-bromo-2-hexene
In acidic solution, a hydrogen will be added to the hydroxy group of the given compound. This intermediate is a good leaving group. As it leaves, a hydrogen will be abstracted and a double bond will form. The bond is across carbons two and three becasue those two are more highly substituted than carbon 1, which is primary. The naming begins at the double bond, so the name is 4-bromo-2-hexene.
Example Question #19 : Carbonyl Reactants

Which reagent(s) would achieve the given synthetic transformation?
PCC
Chromic acid (formed in-situ via ), the correct answer, is a powerful oxidizing agent that converts primary alcohols to carboxylic acids. PCC is also an oxidizing agent, but oxidizes primary alcohols one "rung" up the ladder to aldehydes. , and are reducing agents, which react in the opposite direction of the given transformation.
Example Question #21 : Carbonyl Reactants
What is the product of the following reaction?
The key to answering this question is to realize that potassium permanganate is a very powerful oxidizing agent. Therefore, the primary alcohol in the reactant will be completely oxidized into a carboxylic acid. It's also important to note that because potassium permanganate is such a powerful oxidizing agent, the primary alcohol will not just stop at the aldehyde level of oxidation, but will go all the way to a carboxylic acid, which is at the highest oxidation level.
Example Question #1 : Help With Alcohol Reactions
Which of the following compounds should be used to convert isopropyl alcohol to isopropyl bromide?

or thionyl bromide is used to convert secondary alcohols to the bromide product as shown. Isopropyl alcohol is a secondary alcohol because the alcohol group is bonded to a carbon that is bonded to two other carbons.
The following reaction is the bromination of a secondary alcohol:

Example Question #21 : Carbonyl Reactants
When ethanol is reacted with (sulfuric acid), an ether forms. What is the identity of the ether formed?
Ethanal
1-Ethyne
1-Ethene
Diethyl ether
1-Propene
Diethyl ether
The correct answer is diethyl ether because this is the only ether compound listed.

Diethyl ether forms with the addition of a strong acid to ethanol.
Example Question #584 : Organic Chemistry
Which of the following molecules are capable of being converted into an aldehyde in one step?





In this question, we're being asked to identify which structure can be converted into an aldehyde in one step.
Now, let's remember what an aldehyde is. Aldehydes, along with ketones, are a carbonyl functional group. This means that it contains a carbon doubled bonded to an oxygen. But with aldehydes, the carbon-oxygen double bond is terminal. That is to say, it is at the end of the molecule, because the carbon atom is also bonded to at least one hydrogen atom.
In looking at the structures given in the answer choices, we see that most of them are alcohols. One of them is a ketone, which cannot be converted into an aldehyde in a single step, so this can be ruled out. For the other answer choices, we can see that we have a primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol.
Due to the fact that aldehydes occur at the terminal position of a molecule, we know that if we were to start with an alcohol as our reactant, then it must be a primary alcohol. Thus, the only one that fits this is 
All Organic Chemistry Resources



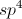
















![CH_{3}(CH_{2})_{2}CH_{2}OH\xrightarrow[]{KMnO_{4}}\: ?](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/463035/gif.latex)














