All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #401 : Biology
Which of the following is not part of the adaptive immune response?
Eosinophils
T-cells
Monocytes
B-cells
Monocytes
The adaptive immune system responds specifically to antigens on the bacteria, virus, or parasite surface. The adaptive immune response includes B- and T-cells, eosinophils, and basophils.
Monocytes differentiate into macrophages in response to infection or injury; they do not respond to specific antigens, and are not involved in the adaptive immune response.
Macrophages phagocytose viruses and bacteria and present their antigens to helper T-cells. Helper T-cells identify the presented antigen and activate B-cells to produce antibodies against the specific antigens. Eosinophils, basophils, additional macrophages, and killer T-cells can then respond to the antibodies to help defend against invading bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Example Question #402 : Biology
Which of the following correctly matches the type of immunity to the way it was recieved?
Passive immunity—having the illness itself
Active immunity—antibody exchange during pregnancy
Passive immunity—intentionally exposing yourself to infected individuals
Active immunity—administering antibodies to a patient
Active immunity—vaccination
Active immunity—vaccination
Active immunity is when you are exposed to a pathogen, either through vaccination, another person with the disease, or any other means, and your body responds by producing specific antibodies with B-cells to destroy the pathogen. Passive immunity is acquired from antibody transfer, so the body does not produce its own antibodies.
Example Question #71 : Immune And Lymphatic Systems
In the crusade to create a vaccine for Poliomyelitis, Jonas Salk and Albert Sabin created two separate vaccines that proved to be successful in preventing Polio onset.
The Salk vaccine, which is given by standard injection, contained virus particles inactivated by an organic solvent. This method has the advantage of inactivating each of the three Polio strains with no bias.
Albert Sabin's vaccine, given by oral inoculation via sugar water, contained live virus particles that had been genetically attenuated. With this method, each of the three Polio strains acquired separate mutations that made them unable to infect the human host cells. Strain 2 in particular contained one single nucleotide polymorphism in the internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) that prevented successful viral replication.
What type of immune response does inoculation with either vaccine stimulate?
Humoral immunity
The adaptive immune response
The lymphatic immune response
The innate immune response
The adaptive immune response
The adaptive immune response is responsible for encountering antigens and creating lasting immunity against it. The humoral immune response plays a role in adaptive immunity, but is more active during the secondary exposure to an antigen.
Example Question #392 : Systems Biology And Tissue Types
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder, resulting in the loss of the dystrophin protein. In healthy muscle, dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma and helps anchor the muscle fiber to the basal lamina. The loss of this protein results in progressive muscle weakness, and eventually death.
In the muscle fibers, the effects of the disease can be exacerbated by auto-immune interference. Weakness of the sarcolemma leads to damage and tears in the membrane. The body’s immune system recognizes the damage and attempts to repair it. However, since the damage exists as a chronic condition, leukocytes begin to present the damaged protein fragments as antigens, stimulating a targeted attack on the damaged parts of the muscle fiber. The attack causes inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis, further weakening the muscle.
Studies have shown that despite the severe pathology of the muscle fibers, the innervation of the muscle is unaffected.
What is the best characterization of the immune response described in the passage?
Initially innate immunity, then adaptive immunity
Innate immunity
Auto-immunity; neither innate nor adaptive immunity describe an autoimmune reaction
Adaptive immunity
Initially adaptive immunity, then innate immunity
Initially innate immunity, then adaptive immunity
The initial response is an effort to repair physical damage, while the chronic response involves the recognition of antigens. Innate immunity refers to the body's natural untargeted defenses, such as the cells that would work to repair damage. Adaptive immunity is targeted to specific pathogens via antigen presentation. Thus, the pattern described in the passage is initially innate immunity, then adaptive immunity.
Example Question #401 : Biology
Inflammation is an important response of the immune system. The vasodilation of blood vessels allows for important cells of the innate immune system to move out of the blood and into the surrounding tissue. Which of the following members of the innate immune system is responsible for causing inflammation at the site of infection?
Macrophages
Dendritic cells
Mast cells
Natural Killer Cells
Mast cells
The correct answer is mast cells. Mast cells as well as granulocytes participate in the innate immune system's inflammatory response. Mast cells release histamine as well as other chemicals that allow for other cells to move from the blood stream into the tissue at the site of infection.
Example Question #402 : Biology
The HIV virus infects which of the following cells in order to diminish coordinated immune responses against pathogens?
Basophils
Macrophages
Neutrophils
Helper T-cells
Cytotoxic T -cells
Helper T-cells
The HIV virus readily attacks Helper T-cells because these cells have a signaling-cascade effect on most immune cells. Most importantly, helper T-cells stimulate B-cells to produce antibodies. As the virus destroys the helper T-cells, it effectively negates the adaptive immune system, making the body exceptionally vulnerable to infection.
Example Question #21 : Adaptive And Innate Immunity
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the loss of tolerance to self antigens leading to the presence of high autoantibody titers. Dysregulated peripheral tolerance and hyperactive germinal centers have been proposed to be one of the driving forces behind the accumulation of high autoantibodies.
What immune cell type is the product of germinal centers and most likely the cell mediating the production of autoantibodies?
Follicular helper T cells
Tingible body macrophages
Follicular dendritic cells
Plasma cells
Natural killer cells
Plasma cells
Plasma cells are the main product of germinal centers and are potent antibody factories. Dysregulated peripheral tolerance and germinal centers can lead to the production of plasma cells that are reactive towards self-nuclear antigens.
Example Question #22 : Adaptive And Innate Immunity
Which of the following is an example of a primary lymphoid organ?
Peyer's patches
Lymph nodes
Tonsils
Thymus
Spleen
Thymus
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ (along with bone marrow). The thymus is where T cells differentiate and mature. All of the other organs listed are secondary lymphoid organs, where lymphocytes reside and respond to antigenic challenges and foreign pathogens.
Example Question #51 : Immune System
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.
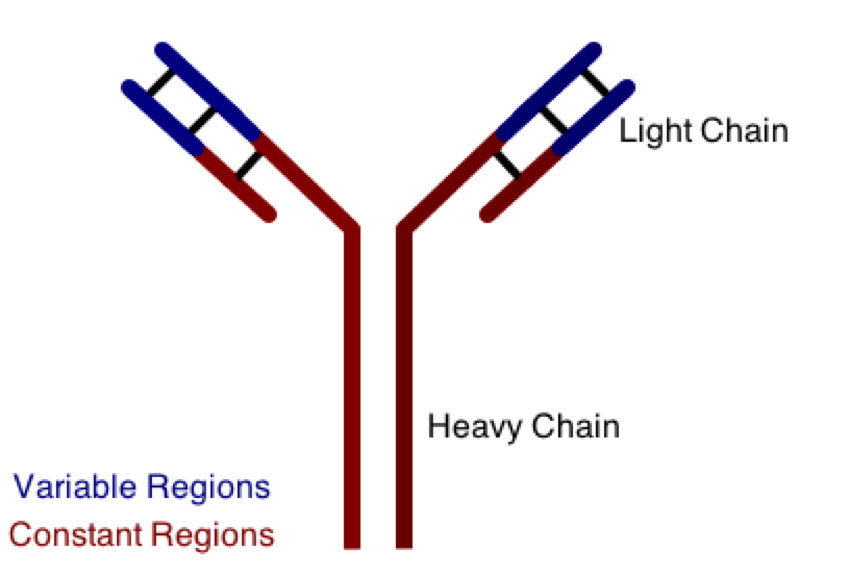
Unlike B-cells, T-cells do not make antibodies. T-cells are important in the execution of cytotoxic immunity, such as neutralizing virus-infected cells. A scientist is studying the T-cell response in a mammal, and finds that his CD8+ T-cells are interacting with a surface protein found on many different types of cells in his model organism. This protein is most likely __________.
a major histocompatibility complex
CCR5
a T-cell receptor
interleukin-2
CD28 ligand
a major histocompatibility complex
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I is found on all nucleated cell types, while MHC class II is limited to antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells. MHC class I presents foreign antigens from intracellular parasites to CD8+ T-cells in an effort to demonstrate infection and initiate cell killing.
C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5) is a specific chemokine receptor on the surface of T-cells, and is involved in cell recruitment to initiate the immune response. CD28 ligand is expressed by antigen-presenting cells and binds to T-cell receptors to activate T-cells. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a cytokine secreted into the blood to help activate the T-cell immune response.
Example Question #404 : Biology
Which of the following combinations might yield the necessity of blood transfusion for a new born baby?
Rh-positive mother and Rh-positive fetus
Rh-negative mother and Rh-positive fetus
Rh-negative mother and Rh-negative fetus
Rh-positive mother and Rh-negative fetus
Rh-negative mother and Rh-positive fetus
Rh factors are surface proteins found on red blood cells. An Rh-negative mother can be exposed to Rh-positive blood from the fetus in her first pregnancy. Without administration of Rh(o) D immunoglobulin during the delivery of her first baby, the mother can develop antibodies to Rh so that during her second pregnancy, the maternal antibodies will cross the placenta and attack the red blood cells of the fetus if it is Rh-positive. The attack on fetal red blood cells will require blood transfusions for the fetus.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources




