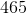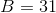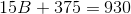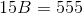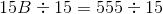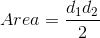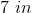All ISEE Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #4 : How To Find The Area Of A Trapezoid
A trapezoid has the base lengths of and . The area of the trapezoid is . Give the height of the trapezoid in terms of .
The area of a trapezoid is given by
,
where , are the lengths of each base and is the altitude (height) of the trapezoid.
Example Question #272 : Plane Geometry
In the following trapezoid and . The area of the trapezoid is 54 square inches. Give the height of the trapezoid. Figure not drawn to scale.

The area of a trapezoid is given by
,
where , are the lengths of each base and is the altitude (height) of the trapezoid.
Substitute these values into the area formula:
Example Question #273 : Plane Geometry

What is the area of the shaded portion of the above square?
Quadrilateral - the shaded region - is a trapezoid with bases and , and altitude . The area of the trapezoid can be calculated using the formula
,
where and , and .
The length of can be found by setting and and applying the Pythagorean Theorem:
Therefore,
.
Substituting:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Trapezoid

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale.
The area of the above trapezoid is . What is ?
Substitute into the formula for the area of a trapezoid:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Kite
Cassie is making a kite for her little brother. She has two plastic tubes to use as the skeleton, measuring inches and inches. If these two tubes represent the diagnals of the kite, how many square inches of paper will she need to make the kite?
To find the area of a kite, use the formula , where represents one diagnal and represents the other.
Since Cassie has one tube measuring inches, we can substitute for . We can also substitute the other tube that measures inches in for .
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Area Of A Kite
Two diagonals of a kite have the lengths of and . Give the area of the kite.
The area of a kite is half the product of the diagonals, i.e.
,
where and are the lengths of the diagonals.
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Area Of A Kite
In the following kite, , and . Give the area of the kite. Figure not drawn to scale.

When you know the length of two unequal sides of a kite and their included angle, the following formula can be used to find the area of a kite:
,
where are the lengths of two unequal sides, is the angle between them and is the sine function.
Example Question #4 : How To Find The Area Of A Kite
Find the area of a kite with one diagonal having length 18in and the other diagonal having a length that is half the first diagonal.
To find the area of a kite, we will use the following formula:
where p and q are the lengths of the diagonals of the kite.
Now, we know the length of one diagonal is 18in. We also know the other diagonal is half of the first diagonal. Therefore, the second diagonal has a length of 9in.
Knowing this, we can substitute into the formula. We get
Example Question #275 : Plane Geometry
A kite has the area of . One of the diagonals of the kite has length . Give the length of the other diagonal of the kite.
The area of a kite is half the product of the diagonals, i.e.
,
where and are the lengths of the diagonals.
Example Question #1 : Parallelograms

Give the area of the above parallelogram if .
Multiply height by base to get the area.
By the 30-60-90 Theorem:
and
The area is therefore
All ISEE Upper Level Math Resources