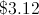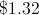All ISEE Middle Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Solve for 
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Solve the following equation if 
In order to solve this problem, we must substitute 

Based on the order of operations we know that we must first deal with the exponents, so we look at 

Next we multiply.
Finally we add subtract.
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Choose the best answer from the four choices given.
If 
then what must 
Notice that 


Thus, 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Choose the best answer from the four choices given.
Richard reaches into his pocket and determines that he has $3.85 in quarters and nickels. When he pulls out his fistful of change, though, he is dismayed to realize that what he thought were quarters are really pennies and what he thought to be nickels are really dimes. If he has 12 pennies, how much is his change worth?
If Richard has 12 pennies, that means that he thought he had 12 quarters ($3.00) and 85 cents worth of nickels (17 nickels). Since what he thought were nickels are really dimes, it means that he has $1.70 worth of dimes to go along with his 12 cents in pennies.
Example Question #5 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Using the information given in each question, compare the quantity in Column A to the quantity in Column B.
Column A Column B
the slope of the y-intercept
this equation of this equation
The quantity in Column B is greater.
The quantity in Column A is greater.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
The two quantities are equal.
The quantity in Column B is greater.
Divide each of the elements of the equation by 5 to get it into 
Thus, the slope is 1.8 and the y-intercept is 2, so B is the correct answer.
Example Question #5 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b)
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(a) is greater
(a) and (b) are equal
(b) is greater
It is impossible to tell from the information given
Rewrite in standard form:
Use the 



Set each linear binomial to 0 and solve:
or
Therefore, it is not clear whether 
Example Question #6 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b)
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(a) is greater
(b) is greater
(a) and (b) are equal
(a) is greater
Rewrite in standard form:
Use the 



Group and solve:
Set each linear binomial to 0 and solve:
or
In either case, 
Example Question #8 : Equations
Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b)
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(a) and (b) are equal
(a) is greater
(b) is greater
It is impossible to tell from the information given
Rewrite in standard form:
Factor the quadratic expression as 


Set each linear binomial to 0 and solve:
Therefore, it is not clear whether 
Example Question #6 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b)
(b) is greater
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(a) is greater
(b) is greater
Rewrite in standard form:
Factor the quadratic expression as 


Set each linear binomial to 0 and solve:
Both solutions are less than 5.
Example Question #7 : How To Find The Solution To An Equation
Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b)
(b) is greater
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(a) is greater
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to tell from the information given
Rewrite in standard form:
Factor the quadratic expression as 


Set each linear binomial to 0 and solve:
It is unclear whether 
All ISEE Middle Level Quantitative Resources