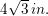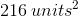All Intermediate Geometry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #21 : Solid Geometry
A geometric cube has a volume of 
The formula for volume of a perfect sphere is represented in this formula, with 
Since we know the volume, we can use the formula for volume to determine length of edges:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Diagonal Of A Cube
Find the diagonal of a cube with a side length of 


The diagonal of a cube is simply given by:
Where 
So since our
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Diagonal Of A Cube
If the volume of a cube was one eighth, what is the diagonal of the cube?
Write the volume of a cube and substitute the given volume to find a side length.
Write the diagonal formula for a cube and substitute the side length.
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Diagonal Of A Cube
Find the length of a diagonal of a cube with volume of
There is a formula for the length of a cube's diagonal given the side length. However, we might not remember that formula as it is less common. However, we can also find the length using the Pythagorean Theorem.
But first, we need to find the side length. We know the volume is 64. Our formula for volume is
Substituting gives
Taking the cube root gives us a side length of 4. Now let's look at our cube.

We need to begin by finding the length of the diagonal of the bottom face of our cube (the green segment). This can be done either by using the Pythagorean Theorem or by realizing that the right triangle is in fact a 45-45-90 triangle. Either way, we realize that our diagonal (the hypotenuse) is 

We now seek to find the diagonal of the cube (the blue segment). We do this by looking at the right triangle formed by it, the left vertical edge, and the face diagonal we just found. This time our only recourse is to do the Pythagorean Theorem.
In general, the formula for the diagonal of a cube with side length 
The length of our diagonal is
Example Question #21 : Cubes
Suppose the volume of a cube is 
Write the equation for the volume of a cube. Substitute the volume to find the side length, 
Write the equation for finding diagonals given an edge length for a cube.
Substitute the side length to find the diagonal length.
The answer is 
Example Question #21 : Solid Geometry
If the volume of a cube was 
Write the equation for finding the volume of a cube, and substitute in the volume.
Write the diagonal equation for cubes and substitute in the given length.
Example Question #21 : Cubes
If the surface area of a cube was 
Write the surface area formula for cubes and substitute the given area.
Write the diagonal formula for cubes and substitute the side length.
Example Question #7 : How To Find The Diagonal Of A Cube
Find the distance from point A to point B in the cube below (leave answer in simplest radical form):

When calculating the diagonal of the cube, point A to point B.
We must first find the diagonal of the base of the cube.
The base of the cube is a square where all sides are 8.
The diagonal of this square is found either by the pythagorean theorem or by what we know about 45-45-90 triangles to get the diagonal of the base below:
The diagonal of the base would be from point A to point C in the drawing.

We can see that the diagonal of the base and side BC of the cube form the two legs of a right triangle that will allow us to find the 3D diagonal of the whole cube.
Use the pythagorean theorem with BC and the Diagonal of the Base.
Take the square root of both sides.
After simplifying everything we get the final answer for the Diagonal of the Cube (AB).
Example Question #8 : How To Find The Diagonal Of A Cube
A cube has a side length of 6 meters. What is the length of its diagonal across one of the faces?
None of these





Since all sides of a cube are equal and all sides form right angles, we use pythagorean theorem to find the length of the diagonal.

Example Question #1 : How To Find The Surface Area Of A Cube
One side of a cube is 
To find the surface area of a cube, we find the area of a face by multiplying two of its sides together; then, we multiply by 


We know that for this problem, 
All Intermediate Geometry Resources


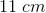




![\\a^3=729\;cm^3\\a=\sqrt[3]{729\;cm^3}\\a=9\;cm](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/751210/gif.latex)