All Intermediate Geometry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Parallel Lines

Which answer contains all the angles (other than itself) that are congruent to Angle 1?
Angles 8 and 6
Angles 4, 5, and 8
Angles 4 and 5
Angles 2 and 5
Angles 2 and 4
Angles 4, 5, and 8
Because of the Corresponding Angles Theorem (Angle 2 and Angle 5), Alternate Exterior Angles (Angle 2 and Angle 8), and Vertical Angles (Angle 2 and Angle 4).
Example Question #2 : Parallel Lines

Angles 2 and 3 are congruent based on which Theorem?
Alternate Interior Angles
Consecutie Internior Angles
Corresponding Angles
Alternate Exteriors Angles
Vertical Angles
Vertical Angles
Veritcal angles means that the angles share the same vertex. Angles 2 and 3 are a vertical pair of angles, which mean that they are congruent.
Example Question #3 : Parallel Lines

If angles 2 and 6 are congruent, lines AB and CD are parallel based on which theorem?
Corresponding Angles
Alternate Exterior Angles
Vertical Angles
Consecutive Interior Angles
Alternate Interior Angles
Corresponding Angles
Angles 2 and 6 are Corresponding Angles. If each of the set of angles were taken separately, angels 2 and 6 would occupy the same place and are thus corresponding angles.
Example Question #4 : Parallel Lines

What is the sum of Angle 3 and Angle 5?
90 deg
45 deg
180 deg
15 deg
360 deg
180 deg
Because of the Consecutive Interior Angle theorem, the sum of Angles 3 and 5 would be 180 deg.
Example Question #5 : Parallel Lines

If lines AB and CD are parallel, angles 1 and 8 are congruent based on which theorem?
Consecutive Interior Angles
Corresponding Angles
Alternate Exterior Angles
Vertical Angles
Alternate Interior Angles
Alternate Exterior Angles
Angles 1 and 8 are on the exterior of the parallel lines and are on opposite sides of the transversal. This means the Theorem is the Alternate Exterior Angle theorem.
Example Question #1 : Parallel Lines

If Angles 2 and 7 are congruent, line AB and CD are __________.
parallel
askance
perpendicular
skew
parallel
Lines AB and CD are parallel based on the Alternate Exterior Angle theorem.
Example Question #6 : Parallel Lines

If lines AB and CD are parallel, angles 5 and 1 are __________.
interior angles
alternate exterior angles
corresponding angles
alternate interior angles
exterior angles
corresponding angles
If the two lines are parallel, the transverse line makes it so that angles 2 and 7 are corresponding angles.
Example Question #1 : How To Find Out If Lines Are Parallel

If lines AB and CD are parallel, the sum of Angle 6 plus Ange 4 equals __________.
15 deg
0 deg
45 deg
90 deg
180 deg
180 deg
If lines AB and CD are parallel, the sum of Angles 4 and 6 is 180 deg based on the Consecutive Interior Angle Theorem.
Example Question #1 : Parallel Lines
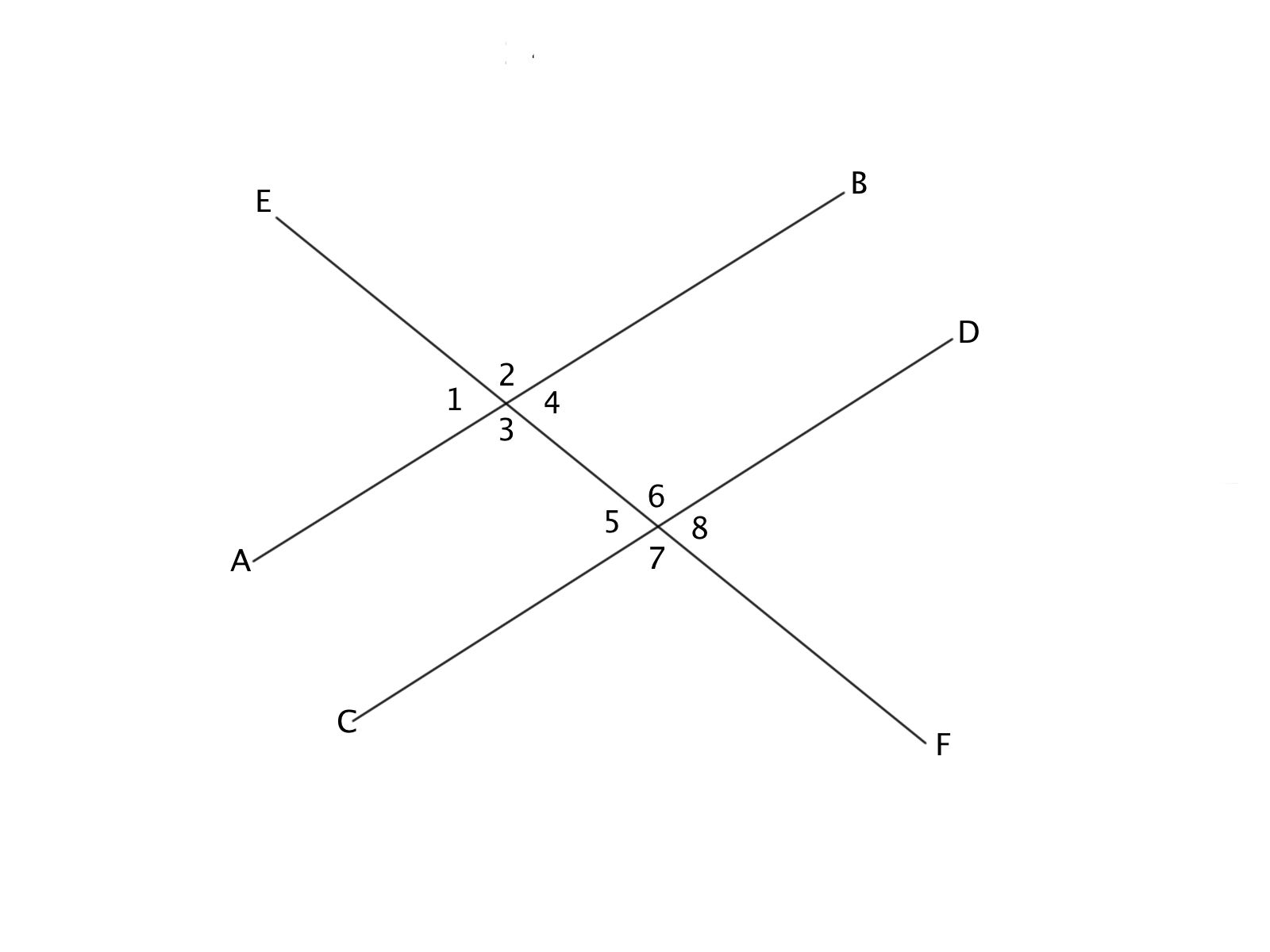
If lines AB and CD are parallel, angles 2 and 7 are congruent based on which theorem?
Alternate Exterior Angles
Alternate Interior Angles
There is not enough information to determine
Consecutive Angles
Corresponding Angles
Alternate Exterior Angles
Angles 2 and 7 are both on the exterior side of the transverse, this means they are Alternate Exterior Angles.
Example Question #1 : How To Find Out If Lines Are Parallel

If lines AB and CD are parallel, which angles are congruent to Angle 3?
Angles 1 and 5
Angles 5, 8, and 1
There is not enought information to determine
Angles 7 and 6
Angles 2, 7, and 6
Angles 2, 7, and 6
Angle 2 is congruent based on the Vertical Angle Theorem. Angle 7 is congruent based on the Corresponding Angles Theorem. Angle 6 is congruent based on the Alternate Interior Angles theorem.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All Intermediate Geometry Resources




