All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #4 : How To Find The Area Of An Equilateral Triangle

An equilateral triangle has a side length of 
Not enough information to solve
In order to find the area of the triangle, we must first calculate the height of its altitude. An altitude slices an equilateral triangle into two 



Therefore, we can find the height of the altitude of this triangle by designating a value for 

that 

Now, we can calculate the area of the triangle via the formula
Now convert to meters.
Example Question #5 : How To Find The Area Of An Equilateral Triangle
Triangle A: A right triangle with sides length 

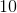
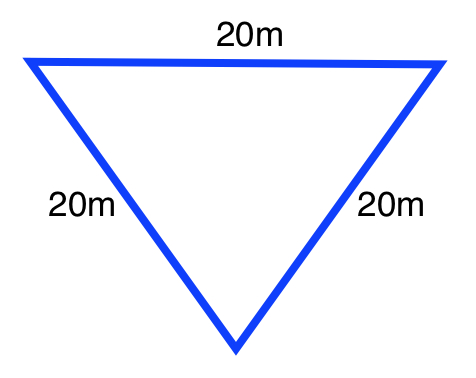
Triangle B: An equilateral triangle with side lengths 
Which triangle has a greater area?
There is not enough information given to determine which triangle has a greater area.
Triangle B
Triangle A
The areas of the two triangles are the same.
Triangle B
The formula for the area of a right triangle is 


The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is 


To determine which of the two areas is greater without using a calculator, rewrite the areas of the two triangles with comparable factors. Triangle A's area can be expressed as 



Example Question #2 : Equilateral Triangles
What is the area of an equilateral triangle with side 11?
Since the area of a triangle is
you need to find the height of the triangle first. Because of the 30-60-90 relationship, you can determine that the height is 
Then, multiply that by the base (11).
Finally, divide it by two to get 52.4.
Example Question #7 : How To Find The Area Of An Equilateral Triangle
Find the area of the following equilateral triangle:
The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is:
Where 
Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of An Equilateral Triangle
Determine the area of the following equilateral triangle:

The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is:

where 
Plugging in our value, we get:
Example Question #11 : Equilateral Triangles
Find the area of an equilateral triangle whose perimeter is
The formula for the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is:
Plugging in our values, we get
The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is:
Plugging in our values, we get
Example Question #153 : Act Math
What is the area of an equilateral triangle with a side length of 5?
Note that an equilateral triangle has equal sides and equal angles. The question gives us the length of the base, 5, but doesn't tell us the height.
If we split the triangle into two equal triangles, each has a base of 5/2 and a hypotenuse of 5.
Therefore we can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the height:
Now we can find the area of the triangle:
Example Question #101 : Triangles
An equilateral triangle has a perimeter of 18. What is its area?
Recall that an equilateral triangle also obeys the rules of isosceles triangles. That means that our triangle can be represented as having a height that bisects both the opposite side and the angle from which the height is "dropped." For our triangle, this can be represented as:

Now, although we do not yet know the height, we do know from our 30-60-90 regular triangle that the side opposite the 60° angle is √3 times the length of the side across from the 30° angle. Therefore, we know that the height is 3√3.
Now, the area of a triangle is (1/2)bh. If the height is 3√3 and the base is 6, then the area is (1/2) * 6 * 3√3 = 3 * 3√3 = 9√(3).
Example Question #472 : Geometry
A circle contains 6 copies of a triangle; each joined to the others at the center of the circle, as well as joined to another triangle on the circle’s circumference.
The circumference of the circle is 
What is the area of one of the triangles?
The radius of the circle is 2, from the equation circumference 
To find the height of this triangle, we must divide it down the centerline, which will make two identical 30-60-90 triangles, each with a base of 1 and a hypotenuse of 2. Since these triangles are both right traingles (they have a 90 degree angle in them), we can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve their height, which will be identical to the height of the equilateral triangle.
We know that the hypotenuse is 2 so 

Now our formula looks like this: 

Let's subtract 1 from each side of that equation, in order to make things a bit simpler:
Now let's apply the square root to each side of the equation, in order to change 

Therefore, the height of our equilateral triangle is
To find the area of our equilateral triangle, we simply have to multiply half the base by the height:
The area of our triangle is
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Height Of An Equilateral Triangle
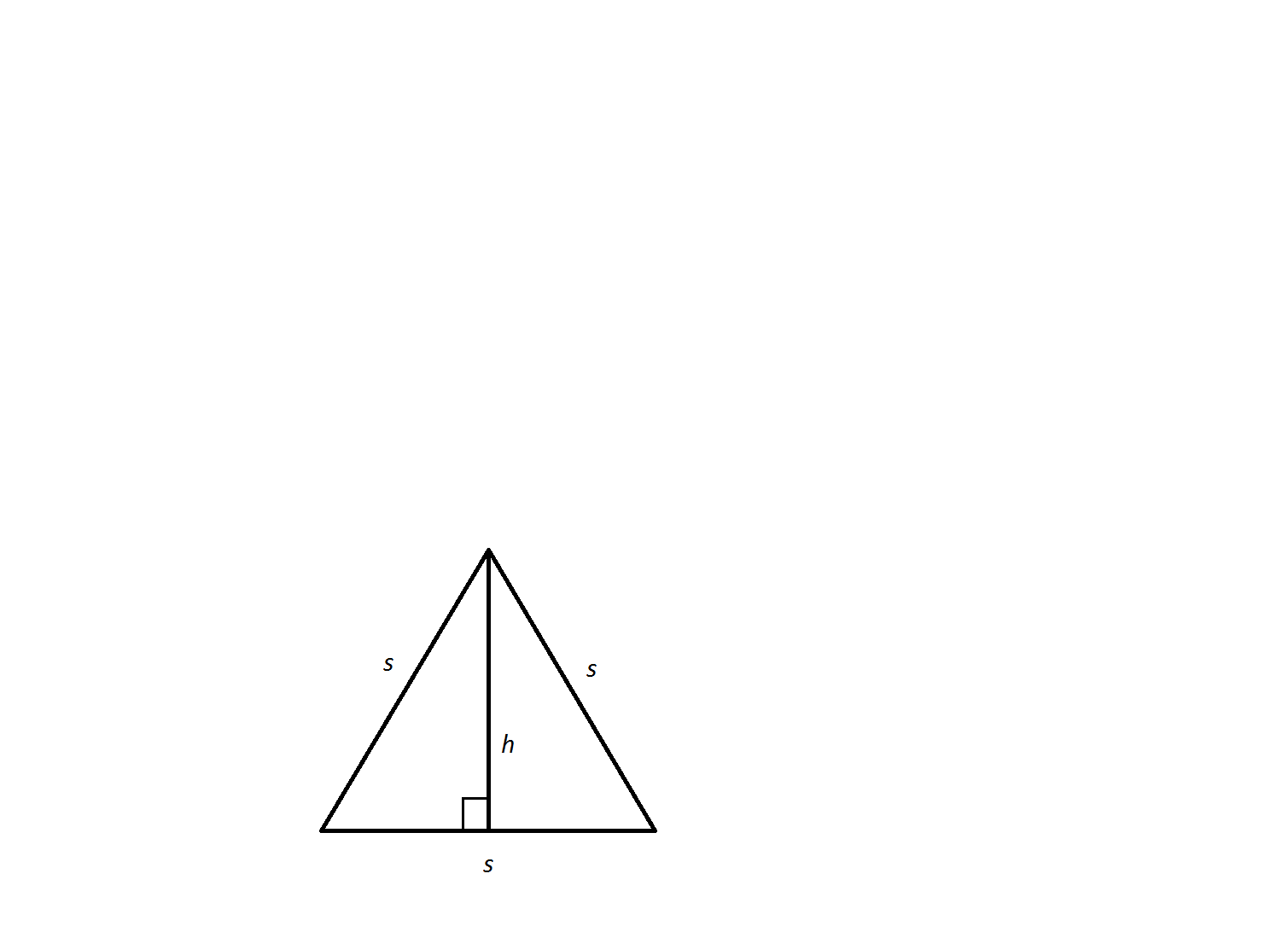
An equilateral triangle has a side length of 

Not enough information to solve
The altitude, 

In a 






In this scenario:
and
Therefore,

Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All High School Math Resources




















































































