All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #12 : Solid Geometry
The surface area of a rectangular prism is 
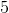
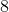
The surface area of a rectangular prism with sides 

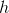

Two sides are known; it does not matter how they are designated, but for this problem let 


Now that the three dimensions are known, it's possible to calculate the volume:
Example Question #321 : Geometry
Quantity A: The length of a side of a cube with a volume of 

Quantity B: The length of a side of a cube with surface area of 

Which of the following is true?
Quantity A is larger.
The relationship between the two quantities cannot be determined.
The two quantities are equal
Quantity B is larger.
The two quantities are equal
Recall that the equation for the volume of a cube is:
Since the sides of a cube are merely squares, the surface area equation is just 
So, for our two quantities:
Quantity A
Use your calculator to estimate this value (since you will not have a square root key). This is 
Quantity B
First divide by 
Therefore,
Therefore, the two quantities are equal.
Example Question #322 : Geometry
What is the length of an edge of a cube with a surface area of 
The surface area of a cube is made up of 



For our data, we know:
This means that:
Now, while you will not have a calculator with a square root key, you do know that 

Example Question #3 : Cubes
If a cube has a total surface area of 
There is not enough information given.


There are 6 sides to a cube. If the total surface area is 54 square inches, then each face must have an area of 9 square inches.
Every face of a cube is a square, so if the area is 9 square inches, each edge must be 3 inches.
Example Question #14 : Solid Geometry
The surface area of a cube is 486 units. What is the distance of its diagonal (e.g. from its front-left-bottom corner to its rear-right-top corner)?
None of the others
81
9√(3)
9
9√(2)
9√(3)
First, we must ascertain the length of each side. Based on our initial data, we know that the 6 faces of the cube will have a surface area of 6x2. This yields the equation:
6x2 = 486, which simplifies to: x2 = 81; x = 9.
Therefore, each side has a length of 9. Imagine the cube is centered on the origin. This means its "front-left-bottom corner" will be at (–4.5, –4.5, 4.5) and its "rear-right-top corner" will be at (4.5, 4.5, –4.5). To find the distance between these, we use the three-dimensional distance formula:
d = √((x1 – x2)2 + (y1 – y2)2 + (z1 – z2)2)
For our data, this will be:
√( (–4.5 – 4.5)2 + (–4.5 – 4.5)2 + (4.5 + 4.5)2) =
√( (–9)2 + (–9)2 + (9)2) = √(81 + 81 + 81) = √(243) =
√(3 * 81) = √(3) * √(81) = 9√(3)
Example Question #323 : Geometry
You have a rectangular box with dimensions 6 inches by 6 inches by 8 inches. What is the length of the shortest distance between two non-adjacent corners of the box?
The shortest length between any two non-adjacent corners will be the diagonal of the smallest face of the rectangular box. The smallest face of the rectangular box is a six-inch by six-inch square. The diagonal of a six-inch square is 
Example Question #1512 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
What is the length of the diagonal of a cube with side lengths of 

The diagonal length of a cube is found by a form of the distance formula that is akin to the Pythagorean Theorem, though with an additional dimension added to it. It is:


Now, if the the value of 

Example Question #4 : Cubes
What is the length of the diagonal of a cube that has a surface area of 

To begin, the best thing to do is to find the length of a side of the cube. This is done using the formula for the surface area of a cube. Recall that a cube is made up of 


Therefore, for our data, we have:
Solving for 
This means that
Now, the diagonal length of a cube is found by a form of the distance formula that is akin to the Pythagorean Theorem, though with an additional dimension added to it. It is:


Now, if the the value of 

Example Question #21 : Solid Geometry
What is the volume of a rectangular box that is twice as long as it is high, and four times as wide as it is long?
8
5L
4L3
2L3
2L2
2L3
The box is 2 times as long as it is high, so H = L/2. It is also 4 times as wide as it is long, so W = 4L. Now we need volume = L * W * H = L * 4L * L/2 = 2L3.
Example Question #324 : Geometry
What is the volume of a cube with a surface area of 

The surface area of a cube is merely the sum of the surface areas of the 


Solving for 

Now, the volume of a cube is defined by the simple equation:
For 
All GRE Math Resources


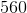


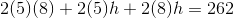

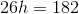

















![3\sqrt[3]{2}in](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/345691/gif.latex)





































