All GMAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #104 : Triangles
The largest angle of an obtuse isosceles triangle has a measure of 

The height of the obtuse isosceles triangle bisects the 






Example Question #1 : Calculating The Area Of An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
What is the area, to the nearest whole square inch, of a triangle with sides 12, 13, and 15 inches?
None of the other answers are correct.
Use Heron's formula:
where 
Example Question #101 : Triangles
Calculate the area of the triangle (not drawn to scale).
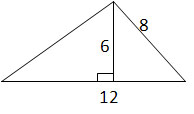
In this problem, the base is 12 and the height is 6. Therefore:
Example Question #102 : Triangles

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale.
What is the area of the above figure?
More information is needed to answer this question.
The figure is a composite of a rectangle and a triangle, as shown:

The rectangle has area
The triangle has area
The total area of the figure is
Example Question #32 : Acute / Obtuse Triangles
Which of the following cannot be the measure of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle?
Each of the other choices can be the measure of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle.
Each of the other choices can be the measure of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle.
The only restriction on the measure of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is the restriction on any angle of a triangle - that it fall between 



Since all of these measures fall in that range, the correct response is that all are allowed.
Example Question #2 : Calculating The Area Of An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
What is the area of the triangle on the coordinate plane formed by the 


The easiest way to solve this is to graph the three lines and to observe the dimensions of the resulting triangle. It helps to know the coordinates of the three points of intersection, which we can do as follows:
The intersection of 


The lines intersect at
The intersection of 


These lines intersect at
The intersection of 

The lines intersect at
The triangle therefore has these three vertices. It is shown below.

As can be seen, it is a triangle with base 9 and height 12, so its area is
Example Question #6 : Calculating The Area Of An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
What is the area of a triangle on the coordinate plane with its vertices on the points 
The vertical segment connecting 





Example Question #7 : Calculating The Area Of An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Which of the following is the area of a triangle on the coordinate plane with its vertices on the points 

We can view the horizontal segment connecting 






Example Question #361 : Geometry
Give the area of a triangle on the coordinate plane with vertices 
This can be illustrated by showing this triangle inscribed inside a rectangle whose vertices are 

The area of the white triangle 
The area of the red triangle:
The area of the green triangle:
And the area of the beige triangle:
The area of the white triangle will be as follows:
Example Question #1 : Calculating The Length Of The Side Of An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Two sides of a triangle measure 5 inches and 11 inches. Which of the following statements correctly expresses the range of possible lengths of the third side 
By the Triangle Inequality, the sum of the lengths of two shortest sides must exceed that of the third.
Case 1: 
Then
Case 2: 
Then 

Therefore, 
All GMAT Math Resources





















































































