All GMAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #561 : Problem Solving Questions
Is it true that 
Suppose you want to answer this question, and you know that 

None of these statements would be sufficient to answer the question.
If you know either that 

If you know that 

If you also know that 
Example Question #562 : Gmat Quantitative Reasoning
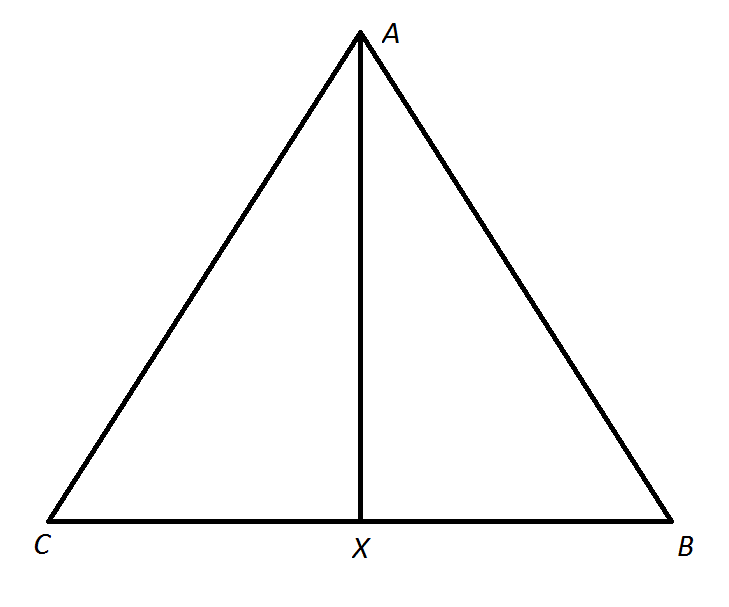
Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale
Refer to the above diagram. Which of the following statements is NOT a consequence of the fact that 






We use the congruence of corresponding sides and angles of congruent triangles to prove four of these statements:








However, nothing in this congruence proves that 


Example Question #562 : Problem Solving Questions
Which of the following cannot be the measure of a base angle of an isosceles triangle?
Each of the other choices can be the measure of a base angle of an isosceles triangle.
An isosceles triangle has two congruent angles by the Isosceles Triangle Theorem; these are the base angles. Since at least two angles of any triangle must be acute, a base angle must be acute - that is, it must measure under 

Example Question #1 : Acute / Obtuse Triangles
Let the three interior angles of a triangle measure 

The triangle is isosceles and obtuse.
The triangle is isosceles and acute.
The triangle is scalene and obtuse.
The triangle is scalene and right.
The triangle is scalene and acute.
The triangle is isosceles and acute.
If these are the measures of the interior angles of a triangle, then they total 

One angle measures 
All three angles measure less than 
Example Question #1 : Calculating An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Two angles of an isosceles triangle measure 


In an isosceles triangle, at least two angles measure the same. Therefore, one of three things happens:
Case 1: The two given angles have the same measure.
The angle measures are 
Case 2: The third angle has measure 
Then, since the sum of the angle measures is 180,
as before
Case 3: The third angle has measure
as before.
Thus, the only possible value of 
Example Question #2 : Calculating An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Two angles of an isosceles triangle measure 


In an isosceles triangle, at least two angles measure the same. Therefore, one of three things happens:
Case 1: The two given angles have the same measure.
This is a false statement, indicating that this situation is impossible.
Case 2: The third angle has measure 
Then, since the sum of the angle measures is 180,
This makes the angle measures 
Case 3: the third angle has measure
Then, since the sum of the angle measures is 180,
This makes the angle measures 
Therefore, either 
Example Question #3 : Calculating An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Which of the following is true of 






By similarity, 
Since measures of the interior angles of a triangle total 
Since the three angle measures of 


Example Question #571 : Gmat Quantitative Reasoning
Which of the following is true of a triangle with three angles whose measures have an arithmetic mean of 
The triangle may be right or obtuse but must be scalene.
The triangle must be obtuse but may be scalene or isosceles.
The triangle must be right and isosceles.
The triangle must be right but may be scalene or isosceles.
The triangle cannot exist.
The triangle cannot exist.
The sum of the measures of three angles of any triangle is 180; therefore, their mean is 
Example Question #5 : Calculating An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Two angles of a triangle measure 

The sum of the degree measures of the angles of a triangle is 180, so we can subtract the two angle measures from 180 to get the third:
Example Question #6 : Calculating An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
The angles of a triangle measure 



The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle total 

All GMAT Math Resources




















































































