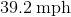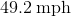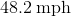All Common Core: High School - Number and Quantity Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #121 : High School: Number And Quantity
Bob is cruising south down a river at , and the river has current due west. What is Bob's actual speed?
Not possible to find
In order to figure this out, we need to create a picture.


Since bob is traveling south, and the current is traveling west, they are perpendicular to each other. This means that they are to each other. The next step is to use the Pythagorean Theorem in order to solve for what speed Bob is actually going.
Recall that the Pythagorean Theorem is , where is the hypotenuse, and , are the legs of the triangle, and have a angle between them.
For our calculations, let , and .
Example Question #2 : Vector Representation Of Quantities (Velocity, Etc.): Ccss.Math.Content.Hsn Vm.A.3
Amanda is cruising north down a river at , and the river has current due east. What is Amanda's actual speed?
In order to figure this out, we need to create a picture.

Since Amanda is traveling north, and the current is traveling east, they are perpendicular to each other. This means that they are to each other. The next step is to use the Pythagorean Theorem in order to solve for what speed Amanda is actually going.
Recall that the Pythagorean Theorem is , where is the hypotenuse, and , are the legs of the triangle, and have a angle between them.
For our calculations, let , and .
Example Question #3 : Vector Representation Of Quantities (Velocity, Etc.): Ccss.Math.Content.Hsn Vm.A.3
Jack slides down a hill at , and throws a rock behind him at . How fast is the rock going?
Since the rock is going in the opposite direction of Jack, we simply subtract the speed of the rock from how fast Jack is going down the hill.
Example Question #4 : Vector Representation Of Quantities (Velocity, Etc.): Ccss.Math.Content.Hsn Vm.A.3
If an airplane is flying south at , and there are winds coming from the west at , how fast is the plane going?
In order to figure this out, we need to create a picture.

Since the airplane is traveling south, and the wind is coming from the west, they are perpendicular to each other. This means that they are to each other. The next step is to use the Pythagorean Theorem in order to solve for what speed the airplane is actually going.
Recall that the Pythagorean Theorem is , where is the hypotenuse, and , are the legs of the triangle, and have a angle between them.
For our calculations, let , and .
Example Question #122 : High School: Number And Quantity
Jill slides down a hill at , and throws a coin forward at . How fast is the coin going?
Since the coin is going in the same direction as Jill, we simply add the speed of the coin and how fast Jill is going down the hill.
Example Question #6 : Vector Representation Of Quantities (Velocity, Etc.): Ccss.Math.Content.Hsn Vm.A.3
Bob slides down a hill at , and throws his wallet behind him at . How fast is his wallet going?
Since Bob's wallet is going in the opposite direction, we simply subtract the speed of the wallet from how fast Bob is going down the hill.
Example Question #1 : Vector Representation Of Quantities (Velocity, Etc.): Ccss.Math.Content.Hsn Vm.A.3
John is cruising north down a river at , and the river has current due east. What is John's actual speed?
In order to figure this out, we need to create a picture.

Since John is traveling north, and the current is traveling east, they are perpendicular to each other. This means that they are to each other. The next step is to use the Pythagorean Theorem in order to solve for what speed John is actually going.
Recall that the Pythagorean Theorem is , where is the hypotenuse, and , are the legs of the triangle, and have a angle between them.
For our calculations, let , and .
Example Question #2 : Vector Representation Of Quantities (Velocity, Etc.): Ccss.Math.Content.Hsn Vm.A.3
Jack slides down a hill at , and throws a rock ahead of him at . How fast is the rock going?
Since the rock is going in the same direction as Jack, we simply add the speed of the rock to how fast Jack is going down the hill.
Example Question #3 : Vector Representation Of Quantities (Velocity, Etc.): Ccss.Math.Content.Hsn Vm.A.3
If an airplane is flying south at , and there are winds going north at , how fast is the plane going?
Since the airplane and the wind are going in opposite directions, we simply subtract the speed of the wind from the speed of the plane.
Example Question #4 : Vector Representation Of Quantities (Velocity, Etc.): Ccss.Math.Content.Hsn Vm.A.3
If an airplane is flying south at , and there are winds going south at , how fast is the plane going?
Since the airplane and the winds are going the same direction, we simply add the airplane and wind speeds together.
All Common Core: High School - Number and Quantity Resources