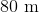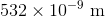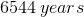All College Physics Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : College Physics
A laser outputs light of a single color with photon energy 
Halving the wavelength is equivalent to doubling the frequency since for a light wave the wavelength and frequency are related by 



Example Question #2 : College Physics
A monochromatic light source is incident on a neutral density filter which decreases the light source's intensity by a factor of 3 but does not change its color. What happens to the energy of a photon in the less intense beam?
The photon energy decreases by a factor of 3.
None of these
The photon energy increases by a factor of 3.
The photon energy decreases only slightly.
The photon energy decreases by a factor of 9.
None of these
The photon energy does not change since the color of light (and therefore the frequency of the light) does not change.
Example Question #1 : Wave Particle Duality
A car with mass 

The de Broglie wavelength is given by 
Example Question #1 : Radioactive Decay
Radiocarbon dating is a method that allows scientists to estimate the age of organisms after they have died. A fairly constant amount of radioactive 




If a scientist finds that a fossil contains 

In this question, we're given a brief description of radiocarbon dating. We're given the amount of 
First, let's briefly go over radiocarbon dating. This method essentially assumes that the amount of radioactive carbon within an organism remains fairly stable at any given time while the organism is alive. Moreover, this amount of radioactive carbon is related to the amount of radioactive carbon in the atmosphere. Once the organism dies, however, it ceases to gain any radioactive carbon; rather, the 


Since we're dealing with the decay of 
We can further rearrange this expression to isolate the variable for time.
In arriving at this expression, we see that we need to know the rate constant, 

Rearranging, we can find the rate-constant.
Now that we have the rate constant, we can plug this value into the previous expression to solve for 
Example Question #2 : Radioactive Decay
Suppose that 



Note: The half-life of the drug is 
For this problem, the first step is to find the rate constant for the decay reaction. Since we're given the half-life, we can calculate this value using the following equation.
Now, we can use the first order rate equation to find out how much drug will be left after the first time interval of 
So, after the first 



With this new amount in mind, we'll need to calculate how much of the drug will be present after more time has elapsed. We can do this by using the same equation as before.
This is the final amount of drug that is expected to be present in the patient's body at that instant of time.
Example Question #1 : Radioactive Decay
Iodine-131 has a half life of 8.02 days and undergoes beta decay.
If a 






Finding the amount is a simple half life problem. Start with setting up what you know for any half-life problem.


From there simplify.

Now plug this into the equation and find what happens after 7 days.
Beta decay is when a neutron releases an electron and becomes a proton. Therefore, the atomic number goes up by one but the atomic mass remains the same. This results in xenon-131.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All College Physics Resources