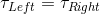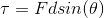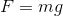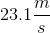All College Physics Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Torque
An object weighing 

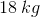
For this question, we'll need to take torque into account. The amount of torque caused by the object to the left of the fulcrum needs to be equal to the torque of the object to the right of the fulcrum.
Moreover, we can write out the equation for torque.
Combining these equations, we can set an expression for the torque on the left and the torque on the right.
Then we can set them equal to each other.
Next, we isolate the term for the distance on the right and we cancel out common units.
Finally, we plug in the values given in the question stem. Because we're told that both objects are sitting flat on the board, we know the force of their weight is perpendicular to the board, which gives a value of 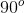
Example Question #51 : Mechanics
Consider the image shown below.

In the container on the left, there is a gas at an unknown pressure. The tubing connected to the container is open to the atmosphere, which has a pressure of 

In this question, we're told that an unknown gas is held within a container. Connected to this container is a tube open to the atmosphere which also contains a liquid. Based on the image shown, the height difference of the liquid levels, and the atmospheric pressure, we're asked to determine the pressure of the unknown gas inside the container.
This is a fairly straight-forward problem that asks us about pressure. Because of the way the tubing is situated, the pressure from the atmosphere will push down on the right side of the tubing, while the pressure from the unknown gas in the container will push down on the left part of the tubing. Since the liquid level on the left is lower than on the right, we can infer that the gas in the container is "pushing" on the liquid more strongly than the atmosphere on the other side. Consequently, we know that the gas in the container has a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure.
The difference in height of the liquid levels allows us to quantitatively determine how much greater this pressure is. Since the height difference shows up as 

Example Question #1 : Fluids
An object is initially submerged 

The absolute pressure slightly decreases
The absolute pressure doubles
The absolute pressure slightly increases
The absolute pressure halves
The absolute pressure slightly increases
For this question, we need to understand the relationship between gauge pressure, ambient pressure, and absolute pressure.
The absolute pressure that an object experiences has two components; ambient and gauge pressure. The ambient pressure is an arbitrarily defined reference pressure that acts on the object. Generally, atmospheric pressure at sea level is used as the reference value, which is 
The equation for absolute pressure can be expressed as follows.
In the above expression, 
But what happens if 


Example Question #1 : Continuity Equation
Fluid flows into a pipe with a diameter of 


This question tests the concept of the continuity equation which stipulates that at steady state the volume flowing into one end of a pipe must be exactly equal to the volume flowing out of the other end. That is, 
Example Question #61 : College Physics
If the radius of a pipe with flowing liquid is decreased by a factor of 
Dcrease by a factor of
Decrease by a factor of
Increase by a factor of
Increase by a factor of
Increase by a factor of
To see how a change of radius affects the velocity of a moving fluid, we'll need to take the continuity equation into account.
Even though the radius is not shown in the above expression, remember that area is related to radius.
Or put another way:
When substituted into the continuity equation:
As the above proportionality shows, if the radius were to decrease by a factor of 


Example Question #1 : Fluids
The reason why a coconut floats in water is because __________.
the surface area of the coconut contacting the water is the same as the surface area of the water contacting the coconut
the gravitational force acting on the coconut is less than the buoyant force
the density of the coconut is equal to the density of the water it displaces
the density of the coconut is less than the density of the water it displaces
the gravitational force acting on the coconut is less than the buoyant force
The equation for the buoyant force is 
Example Question #2 : Density, Specific Gravity, And Viscosity
A baseball has a mass of 


We are given the mass of the baseball outside of the water. Using the weight equation 


The buoyancy force is the difference of the weight of the baseball when it is in the air and when it is in the water. So subtract the two differences:
Now we use the buoyancy equation:





and we get
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All College Physics Resources