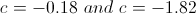All Calculus 1 Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #17 : Points Of Inflection
Where does the function 
The point of inflection of an object can be found by setting the second derivative of the function equal to zero and solving.
Example Question #18 : Points Of Inflection
Find the 

First, we need to simplify the expression. Sine the numerator has more terms than the denominator, we can simply divide out both terms.

Now, we must compute the second derivative of this function, and set it equal to zero.



Example Question #21 : Points Of Inflection
Find the points of inflection for the following function:
To find the points of inflection, we must find the points at which the second derivative of the function changes sign.
First, we must find the second derivative:
The derivatives were found using the following rule:
Next, we must find the x value at which the second derivative is equal to zero:
Using this value, we make our intervals on which we examine the sign of the second derivative:
Note that at the endpoints of the intervals, the second derivative is neither positive nor negative.
Now, simply plug in any value on the interval into the second derivative function and check the sign. On the first interval, the second derivative is negative, while on the second interval, it is positive. Thus, a point of inflection exists at 
The point of inflection is 
Example Question #22 : Points Of Inflection
Determine the points of inflection for the following function:
To determine the points of inflection, we must determine the x values at which the second derivative changes in sign.
So, we must first find the second derivative:
The derivatives were found using the rule
Next, we must find the values at which the second derivative is equal to zero:
Now, using this zero, we can make the intervals on which we check the sign of the second derivative:
Note that at the endpoints, the second derivative is neither positive nor negative.
Plug in any value on each interval into the second derivative function and check the sign. On the first interval, the second derivative is negative, while on the second, it is positive. Because a sign change occured at 
Example Question #23 : Points Of Inflection
Determine the points of inflection for the following function:
To determine the points of inflection of the function, we must determine where the second derivative of the function changes sign.
First, we find the second derivative:
The derivatives were found using the following rule:
Now, we must find where the second derivative equals zero:
Using this value, we can now create the intervals on which we check the sign of the second derivative:
Note that at the endpoints of the intervals, the second derivative is neither positive nor negative.
To check the second derivative's sign on each interval, simply plug in any point on the interval into the second derivative function. On the first interval, the second derivative is negative, while on the second interval, it is positive. Because the sign of the second derivative changes at 
Example Question #3 : Derivatives
What are the 
There are no points of inflection on this graph.
Infelction points are the points of a graph where the concavity of the graph changes. The inflection points of a graph are found by taking the double derivative of the graph equation, setting it equal to zero, then solving for 
To take the derivative of this equation, we must use the power rule,

We also must remember that the derivative of an constant is 0.
After taking the first derivative of the graph equation using the power rule, the equation becomes

In this problem the double derivative of the graph equation comes out to 

Solving for 

Example Question #1 : Other Points
Find the critical points (rounded to two decimal places):
To find the critical points, set 

Differentiate:
Set equal to zero:
Solve for 
Example Question #101 : Graphing Functions
Find the 

There are no real answers.
In order to find the critical points, we must find 
Set
Use the quadratic equation to solve for 
Remember that the quadratic equation is as follows.

equation 
In this case, 


After plugging in those values, we get

So the critical points 
Example Question #102 : Graphing Functions
Find the 

In order to find the critical points, we must find 

Set 
Use the quadratic equation to solve for 
Remember that the quadratic equation is as follows.


In this case, 


After plugging in those values, we get.

So the critical points 
Example Question #103 : Graphing Functions
Find the critical points of
The critical points are complex.
First we need to find 
Now we set
Now we can use the quadratic equation in order to find the critical points.
Remember that the quadratic equation is

where a,b,c refer to the coefficients in the equation
In this case, a=3, b=6, and c=1.
Thus are critical points are
All Calculus 1 Resources