All Basic Geometry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1134 : Basic Geometry
Find the perimeter.


Notice that the given triangle is a right isosceles triangle. The two legs with the tick marks are the same length.
The lengths of the legs in the given triangle are then 
Next, find the length of the hypotenuse by using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Plug in the value of the length of a leg to find the length of the hypotenuse.
Finally, recall how to find the perimeter of a triangle:
Plug in the values for this triangle to find its perimeter.
Make sure to round to two places after the decimal.
Example Question #31 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A 45/45/90 Right Isosceles Triangle
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.
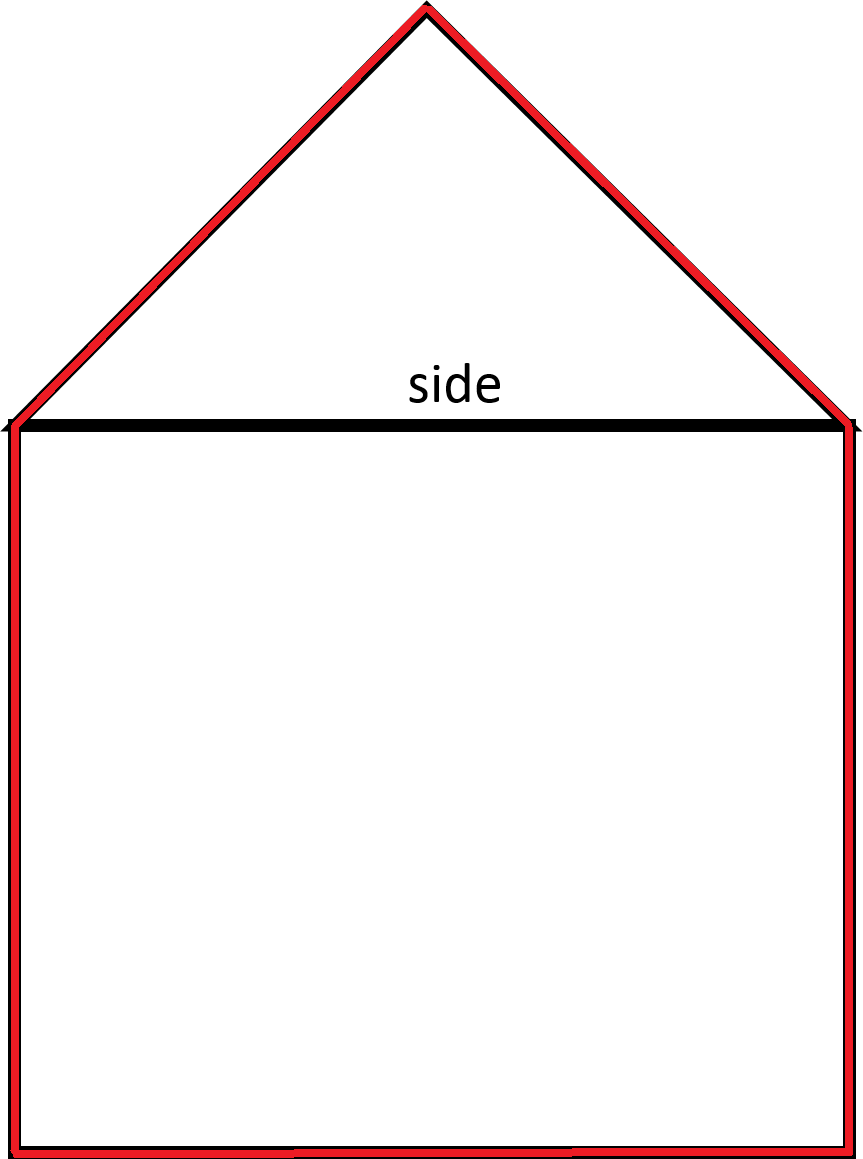
In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Example Question #32 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A 45/45/90 Right Isosceles Triangle
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.

In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Example Question #33 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A 45/45/90 Right Isosceles Triangle
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.

In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Example Question #151 : 45/45/90 Right Isosceles Triangles
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.

In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Example Question #35 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A 45/45/90 Right Isosceles Triangle
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.

In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Example Question #1131 : Basic Geometry
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.

In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Example Question #37 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A 45/45/90 Right Isosceles Triangle
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.

In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Example Question #38 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A 45/45/90 Right Isosceles Triangle
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.

In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Example Question #39 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A 45/45/90 Right Isosceles Triangle
A right isosceles triangle is stacked on top of a square as shown in the figure. Find the perimeter of the compound shape.


Notice that the hypotenuse of the right isosceles triangle is also the length of a side of the square.
First, we will need to find the length of the legs of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem.
Substitute in the given length of the hypotenuse to find the length of the leg of the triangle.

In order to find the perimeter, add up the lengths outlined in red. The perimeter includes the two legs of the triangle and three sides of the square.
Therefore:
Certified Tutor
All Basic Geometry Resources


























































































































