All AP Statistics Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #11 : Estimation
|
Subject |
Horn Length (in) |
Subject |
Horn Length (in) |
|
1 |
19.1 |
11 |
11.6 |
|
2 |
14.7 |
12 |
18.5 |
|
3 |
10.2 |
13 |
28.7 |
|
4 |
16.1 |
14 |
15.3 |
|
5 |
13.9 |
15 |
13.5 |
|
6 |
12.0 |
16 |
7.7 |
|
7 |
20.7 |
17 |
17.2 |
|
8 |
8.6 |
18 |
19.0 |
|
9 |
24.2 |
19 |
20.9 |
|
10 |
17.3 |
20 |
21.3 |
The data above represents measurements of the horn lengths of African water buffalo that were raised on calcium supplements. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population mean for horn length after supplments.
First you must calculate the sample mean and sample standard deviation of the sample.
Because we do not know the population standard deviation we will use the t-distribution to calculate the confidence intervals. We must use standard error in this formula because we are working with the standard deviation of the sampling distribution.
Formula:
To find the appropriate t-value for 95% confidence interval:
Look up 
Thus the 95% confidence interval is:
Example Question #51 : Ap Statistics
The population standard deviation is 7. Our sample size is 36.
What is the 95% margin of error for:
1) the population mean
2) the sample mean
1) 14.567
2) 4.445
1) 15.554
2) 3.656
1) 12.266
2) 3.711
1) 13.720
2) 2.287
1) 11
2) 3
1) 13.720
2) 2.287
For 95% confidence, Z = 1.96.
1) The population M.O.E. =

2) The sample standard deviation =
The sample M.O.E. =
Example Question #611 : Gre Subject Test: Math
The 

What does the confidence interval tell us about the difference in the two programs?


Zero is in the interval, so do not reject the null. There is no evidence that one program is better than the other.
The confidence interval is large, so one program is clearly better at reducing mile times than the other.
The mean improvement of 

Zero is not in the interval, so reject the null. This is evidence that one program is significantly better at reducing mile times.
Zero is in the interval, so do not reject the null. There is no evidence that one program is better than the other.
For there to be a statistically significant difference in the training programs, the 95% confidence interval cannot include zero. 
Example Question #8 : Confidence Intervals
Example Question #9 : Confidence Intervals
Example Question #10 : Confidence Intervals
In a simple random sample of 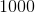


The sample is not sufficiently large. A confidence interval cannot be used.
Step 1: Determine the approporiate formula. In this case, the statistic is a proportion because the question says 261 people out of 1000 are left-handed. We want to use a confidence interval for proportions. The equation is
Step 2: 
Step 3: The questions asks for a 95% confidence interval. You can assume a normal distribution because of the large sample size. Therefore, in a normal distribution, 95% of the data is contained within 
Step 4: Substitue all the values into the equation to get the answer.
Example Question #1 : How To Find Confidence Intervals For A Proportion
A health insurance executive suspects that 50% of insurance applications are incomplete (i.e. critical data is missing from the application). He wants to gather a sample to estimate the true proportion. He wants to be within 5% of the true mean with 95% confidence.
What sample size does he need?
395
365
375
385
405
385
Example Question #1 : How To Find Confidence Intervals For The Slope Of A Least Squares Regression Line
You estimate a regression model with 



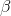
To construct 95% confidence intervals for 



Example Question #61 : Ap Statistics
Which of the following statements are correct about confidence intervals?
The width of a confidence interval increases as the sample size increases and increases as the confidence level increases.
The width of a confidence interval does not change as the sample size increases and increases as the confidence level increases.
The width of a confidence interval decreases as the sample size increases and increases as the confidence level decreases.
The width of a confidence interval decreases as the sample size increases and increases as the confidence level increases.
The width of a confidence interval increases as the sample size increases and increases as the confidence level decreases.
The width of a confidence interval decreases as the sample size increases and increases as the confidence level increases.
Larger samples give narrower intervals. We are able to estimate a population proportion more precisely with a larger sample size.
As the confidence level increases the width of the confidence interval also increases. A larger confidence level increases the chance that the correct value will be found in the confidence interval. This means that the interval is larger.
Example Question #61 : Ap Statistics
You are asked to create a 


Keep in mind that the margin of error for a confidence interval based on a normal population is equal to 


From the problem, we can tell that 


The minimum sample size is 



Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All AP Statistics Resources
























![\left [ 3.1,3.45 \right ]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/37121/gif.latex)
![\left [ 3.4,3.45 \right ]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/37120/gif.latex)
![\left [ 3.35,3.45 \right ]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/37119/gif.latex)












