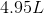All AP Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Stoichiometry With Reactions
Consider the reaction of baking soda and vinegar in an aqueous solution:
If we begin with 17g of 

Assume that all gases behave as ideal gases at atmospheric pressure. The temperature is 298K.
We begin with 17 g of

Now with the molecular weight, we will calculate the number of moles within 17 g of 
Now we will use this to calculate the number of moles of gas produced. In this reaction, the only gas produced is carbon dioxide.
An ideal gas at 1 atmosphere and 298 K has the molar volume of 
Example Question #2 : Stoichiometry With Reactions
What volume of 0.5M NaOH is necessary to neutralize 15mL of 1.0M nitrous acid?
30mL
1L
30L
10mL
30mL
Both the acid and the base provide one equivalent of the necessary ions (H+ and OH–, respectively) and therefore you can use the equation M1V1 = M2V2.
(1)(15) = (0.5)V2
V2 = 30mL
Example Question #31 : Stoichiometry
What volume of 0.5M Mg(OH)2 is necessary to neutralize 15mL of 1.0M nitrous acid?
10mL
15L
30mL
15mL
1L
30mL
This problem is tricky because you must realize that Mg(OH)2 will release 2 molecules of OH– whenever one dissolves; thus, you only need half the amount of Mg(OH)2 to neutralize all of the nitrous acid, which only gives 1 equivalent.
M1V1 = M2V2
Plugging in the values, you get 30mL, but in reality you only need half of that amount.
Example Question #1 : Stoichiometry With Reactions
Magnesium will combine with oxygen gas to form magnesium oxide according to the balanced equation below.
If 65g of MgO are created in the reaction, how many grams of magnesium are used in the reaction?
In order to determine how many grams of magnesium are used in the reaction, we can use the percentage by mass of magnesium in MgO in order to find out how much magnesium is in 65 grams of MgO. The molar mass of MgO is 40.3 grams. The molar mass of magnesium is 24.3 grams. Dividing 24.3 by 40.3 reveals that magnesium makes up 60% of the mass of MgO.
Multiplying 65 grams by 0.603 reveals that there are 39.2 grams of magnesium in 65 grams of MgO.
An alternative means of solving the problem would be to convert grams of MgO to moles. The ratio of MgO to Mg in the given chemical equation is 2:2, thus the number of moles of MgO formed is equal to the number of moles of Mg reacted. Once this number is found, it can be converted back to grams using the molar mass of magnesium.
Example Question #2 : Stoichiometry With Reactions
Consider the following chemical reaction:
How many moles of 
None of the available answers
There is not enough information to answer this question
1.56 moles
1.39mol
4.17mol
1.39mol
This problem is solved based on stoichiometry. Using the molecular weights and ratios in the given reaction, we can solve for the amount of 
Example Question #3 : Stoichiometry With Reactions
The formation of ammonia is given by the following equation:
Assuming you started with 20g of hydrogen gas, how much nitrogen gas is necessary to react the hydrogen gas?
40g
6.67g
93.33g
60g
93.33g
We can convert the mass of hydrogen from grams to moles by using the equation moles = mass / molar mass
Now that we have the moles of hydrogen, we can use the molar ratio given in the equation of 1:3. Since we need 1/3 of the moles of hydrogen as nitrogen, we know we need 3.33 moles of nitrogen gas.
Now, we simply multiply the moles by the molar mass of nitrogen gas (28 grams per mol) and we find we need 93.33 grams of nitrogen gas.
Example Question #2 : Stoichiometry With Reactions
The formation of ammonia is given by the following equation:
Assuming you start with 15mol of hydrogen gas, how many moles of nitrogen gas will be needed to completely react the hydrogen gas?
Since the amount of hydrogen gas is given in moles, this solution is as easy as using the molar ratio between the reactants. Looking at the equation, we see that there is a 1:3 ratio for nitrogen to hydrogen. As a result, we would need one third of the amount of hydrogen available in order to use up all of the hydrogen gas.
Example Question #3 : Stoichiometry With Reactions
How many moles of water vapor will be formed when 5.00g of hydrogen gas react with excess oxygen?
When dealing with questions related to stoichiometry, it is important to compare only mole-to-mole ratios.
Hydrogen gas is diatomic. When converting grams to moles, we will need to double the atomic mass of hydrogen.
We now know we have 2.5 moles of hydrogen gas. Now we need to write a balanced equation to determine the conversion factor between hydrogen gas and the product.
For every two moles of hydrogen consumed, two moles of water are produced. Using this ratio and the starting moles of hydrogen, we can calculate the moles of water produced.
Example Question #4 : Stoichiometry With Reactions
What volume of chlorine gas at 
There is not enough information to answer this question
First, we need to solve for the moles of chlorine gas needed to react with the full amount of sodium metal.
Now, using the ideal gas law, we can solve for the volume that this gas would occupy at the given temperature and pressure.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All AP Chemistry Resources