All ACT Science Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #2 : How To Find Synthesis Of Data In Chemistry
Both gases and liquids are considered to be fluids that have individual molecules that move around with kinetic and potential energy. Kinetic energy, defined as the energy related to motion, takes three forms: translational energy that occurs as a molecule moves from position A to position B, rotational energy that occurs as a molecule spins around an imaginary axis at its center of mass, and vibrational energy that occurs as individual atoms in a molecular bond move towards and away from each other. Usually, molecules possess varying combinations of kinetic energy forms. In contrast, potential energy is defined as stored energy that could be released to become kinetic energy. The total energy of a molecule is fixed, meaning that a molecule has some combination of kinetic and potential energies.
Varying amount of kinetic and potential energies define how molecules in a fluid interact with each other. For example, when the kinetic energy of a molecule is high (greater than 1000J), it can no longer interact with neighboring molecules strongly enough to remain a liquid. However, if the potential energies are too high (greater than 1000 J), molecules cannot escape a liquid to become a gas. If the kinetic energy is high and the potential energy is low, molecules tend to become a gas and can be modeled by an equation known as the Ideal Gas Law:
Where P is the pressure of a gas, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of a gas, R is a constant, and T is temperature in degrees Kelvin.
The Ideal Gas Law perfectly applies to particles with no mass, no intermolecular interactions, and no true volume. However, real molecules do not adhere perfectly to the Ideal Gas Law.
At a constant temperature, the relationship between pressure and volume is best illustrated as:





Using the provided formula, we see that at a fixed temperature, pressure is inversely proportional to volume. They are on the same side of the equals sign, but can better be equated by rearranging the equation as: 
Example Question #3 : How To Find Synthesis Of Data In Chemistry
Chemists can model how solids, liquids, and gases behave at different temperatures and pressures with a graph called a phase diagram. When the pressure and temperature are simultaneously known, a scientist can predict whether the material will be in a specific state. The diagram is divided into sections depending on the phase and the lines between sections represent phase transitions occurring between two or more separate phases.
In general, solids of neatly stacked molecules exist when temperatures are low and pressures are intermediate. These values decrease the kinetic energy of the molecules enough to allow for attractive forces to begin the stacking process. Liquids, by contrast, are found at intermediate pressures and temperatures. The temperature is high enough to impart enough kinetic energy to prevent solid formation and the pressure is high enough to prevent the liquid from becoming a gas. Finally, a gas forms at low pressures and high temperatures. The high level of kinetic energy prevents molecules from associating with one another.
Materials can undergo processes called phase transitions, meaning they can transition from one phase to another. The transition from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while the reverse transition is called freezing. Vaporization occurs when a liquid becomes a gas, while condensation occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. Finally, in a process called sublimation, a solid can directly become a gas without passing through a liquid phase. Additionally, when a gas directly becomes a solid, this is known as deposition.

The process as a substance goes from its phase in area one to its new phase in area two is called __________.
Vaporization
Melting
Condensation
Freezing
Melting
Paragraphs two and three in the passage help us answer this question. Using the information contained in paragraph two, we are able to determine that area one corresponds to the solid phase (low temperature and intermediate pressure) and area two corresponds to the liquid phase (intermediate pressures and temperatures). Thus, we are transitioning between the solid and liquid phases. According to paragraph three, this process is called melting.
Example Question #791 : Act Science
Chemists can model how solids, liquids, and gases behave at different temperatures and pressures with a graph called a phase diagram. When the pressure and temperature are simultaneously known, a scientist can predict whether the material will be in a specific state. The diagram is divided into sections depending on the phase and the lines between sections represent phase transitions occurring between two or more separate phases.
In general, solids of neatly stacked molecules exist when temperatures are low and pressures are intermediate. These values decrease the kinetic energy of the molecules enough to allow for attractive forces to begin the stacking process. Liquids, by contrast, are found at intermediate pressures and temperatures. The temperature is high enough to impart enough kinetic energy to prevent solid formation and the pressure is high enough to prevent the liquid from becoming a gas. Finally, a gas forms at low pressures and high temperatures. The high level of kinetic energy prevents molecules from associating with one another.
Materials can undergo processes called phase transitions, meaning they can transition from one phase to another. The transition from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while the reverse transition is called freezing. Vaporization occurs when a liquid becomes a gas, while condensation occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. Finally, in a process called sublimation, a solid can directly become a gas without passing through a liquid phase. Additionally, when a gas directly becomes a solid, this is known as deposition.

Which phase transition occurs as a material transitions from area two to area three in the figure?
Melting
Condensation
Vaporization
Freezing
Vaporization
Using paragraph two, we can determine that area two corresponds to a liquid (intermediate temperatures and pressures) and area three corresoonds to a gas (high temperature and low pressure). According to paragraph three, this process is called vaporization.
Example Question #111 : Chemistry
Chemists can model how solids, liquids, and gases behave at different temperatures and pressures with a graph called a phase diagram. When the pressure and temperature are simultaneously known, a scientist can predict whether the material will be in a specific state. The diagram is divided into sections depending on the phase and the lines between sections represent phase transitions occurring between two or more separate phases.
In general, solids of neatly stacked molecules exist when temperatures are low and pressures are intermediate. These values decrease the kinetic energy of the molecules enough to allow for attractive forces to begin the stacking process. Liquids, by contrast, are found at intermediate pressures and temperatures. The temperature is high enough to impart enough kinetic energy to prevent solid formation and the pressure is high enough to prevent the liquid from becoming a gas. Finally, a gas forms at low pressures and high temperatures. The high level of kinetic energy prevents molecules from associating with one another.
Materials can undergo processes called phase transitions, meaning they can transition from one phase to another. The transition from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while the reverse transition is called freezing. Vaporization occurs when a liquid becomes a gas, while condensation occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. Finally, in a process called sublimation, a solid can directly become a gas without passing through a liquid phase. Additionally, when a gas directly becomes a solid, this is known as deposition.

The phase transition occuring at Point C where a substance moves from area one to area three is called __________.
Condensation
Sublimation
Vaporization
Deposition
Sublimation
Paragraph three helps us understand that sublimation occurs when a substance transitions from the solid phase directly to the gaseous phase. Using the information also provided in paragraph two, we can see that area one is where the substance is in solid form (low temperature with intermediate pressure) and area three is where the substance is in gaseous form (high temperature and low pressure).
Example Question #112 : Chemistry
Chemists can model how solids, liquids, and gases behave at different temperatures and pressures with a graph called a phase diagram. When the pressure and temperature are simultaneously known, a scientist can predict whether the material will be in a specific state. The diagram is divided into sections depending on the phase and the lines between sections represent phase transitions occurring between two or more separate phases.
In general, solids of neatly stacked molecules exist when temperatures are low and pressures are intermediate. These values decrease the kinetic energy of the molecules enough to allow for attractive forces to begin the stacking process. Liquids, by contrast, are found at intermediate pressures and temperatures. The temperature is high enough to impart enough kinetic energy to prevent solid formation and the pressure is high enough to prevent the liquid from becoming a gas. Finally, a gas forms at low pressures and high temperatures. The high level of kinetic energy prevents molecules from associating with one another.
Materials can undergo processes called phase transitions, meaning they can transition from one phase to another. The transition from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while the reverse transition is called freezing. Vaporization occurs when a liquid becomes a gas, while condensation occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. Finally, in a process called sublimation, a solid can directly become a gas without passing through a liquid phase. Additionally, when a gas directly becomes a solid, this is known as deposition.

The phase transition occuring at Point A where a substance goes from its phase in area two to its phase in area one is best described as __________.
Freezing
Vaporization
Boiling
Condensation
Freezing
Paragraph three helps us understand that as a material transitions from a liquid to a solid, it is freezing. We can determine that area two is the liquid phase by noting that it is at intermediate pressure and temperature. Additionally, we can determine that area one is a solid by noting the low temperature and intermediate pressure.
Example Question #113 : Chemistry
Chemists can model how solids, liquids, and gases behave at different temperatures and pressures with a graph called a phase diagram. When the pressure and temperature are simultaneously known, a scientist can predict whether the material will be in a specific state. The diagram is divided into sections depending on the phase and the lines between sections represent phase transitions occurring between two or more separate phases.
In general, solids of neatly stacked molecules exist when temperatures are low and pressures are intermediate. These values decrease the kinetic energy of the molecules enough to allow for attractive forces to begin the stacking process. Liquids, by contrast, are found at intermediate pressures and temperatures. The temperature is high enough to impart enough kinetic energy to prevent solid formation and the pressure is high enough to prevent the liquid from becoming a gas. Finally, a gas forms at low pressures and high temperatures. The high level of kinetic energy prevents molecules from associating with one another.
Materials can undergo processes called phase transitions, meaning they can transition from one phase to another. The transition from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while the reverse transition is called freezing. Vaporization occurs when a liquid becomes a gas, while condensation occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. Finally, in a process called sublimation, a solid can directly become a gas without passing through a liquid phase. Additionally, when a gas directly becomes a solid, this is known as deposition.

At Point D, the material is most likley in what phase(s)?
Solid
Liquid
Solid, Liquid, and Gas
Gas
Solid, Liquid, and Gas
The last sentence of the first paragraph gives us an indication of what Point D may represent. We are told that the lines between sections represents a phase transition occuring between those respective phases. At Point D, however, we see that all three phases intersect, implying that all phase transitions are occuring simulaneously at this point and thus all states of the material may be present.
Example Question #114 : Chemistry
Chemists can model how solids, liquids, and gases behave at different temperatures and pressures with a graph called a phase diagram. When the pressure and temperature are simultaneously known, a scientist can predict whether the material will be in a specific state. The diagram is divided into sections depending on the phase and the lines between sections represent phase transitions occurring between two or more separate phases.
In general, solids of neatly stacked molecules exist when temperatures are low and pressures are intermediate. These values decrease the kinetic energy of the molecules enough to allow for attractive forces to begin the stacking process. Liquids, by contrast, are found at intermediate pressures and temperatures. The temperature is high enough to impart enough kinetic energy to prevent solid formation and the pressure is high enough to prevent the liquid from becoming a gas. Finally, a gas forms at low pressures and high temperatures. The high level of kinetic energy prevents molecules from associating with one another.
Materials can undergo processes called phase transitions, meaning they can transition from one phase to another. The transition from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while the reverse transition is called freezing. Vaporization occurs when a liquid becomes a gas, while condensation occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. Finally, in a process called sublimation, a solid can directly become a gas without passing through a liquid phase. Additionally, when a gas directly becomes a solid, this is known as deposition.

Solid carbon dioxide is commonly stored in freezing cold, low pressure rooms to prevent loss of the material. If the temperature in the room slowly warmed, the solid carbon dioxide would most likely become what?
Gas
Remain Solid
Cannot Be Determined
Liquid
Gas
This question asks us to look at the figure to see what would happen if we keep the pressure constant but increase the temperature of the room storing the dry ice. We can see that as we move left to right across the figure, without changing pressure, that we cross the phase transition line for sublimation/deposition. Becasue the temperature is warming, we know we are going from a solid directly to a gas by the process of sublimation.
Example Question #115 : Chemistry
Chemists can model how solids, liquids, and gases behave at different temperatures and pressures with a graph called a phase diagram. When the pressure and temperature are simultaneously known, a scientist can predict whether the material will be in a specific state. The diagram is divided into sections depending on the phase and the lines between sections represent phase transitions occurring between two or more separate phases.
In general, solids of neatly stacked molecules exist when temperatures are low and pressures are intermediate. These values decrease the kinetic energy of the molecules enough to allow for attractive forces to begin the stacking process. Liquids, by contrast, are found at intermediate pressures and temperatures. The temperature is high enough to impart enough kinetic energy to prevent solid formation and the pressure is high enough to prevent the liquid from becoming a gas. Finally, a gas forms at low pressures and high temperatures. The high level of kinetic energy prevents molecules from associating with one another.
Materials can undergo processes called phase transitions, meaning they can transition from one phase to another. The transition from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while the reverse transition is called freezing. Vaporization occurs when a liquid becomes a gas, while condensation occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. Finally, in a process called sublimation, a solid can directly become a gas without passing through a liquid phase. Additionally, when a gas directly becomes a solid, this is known as deposition.

What property most likely allows for molecules to stack neatly when freezing?
Increase in Potential Energy
Symmetric Molecules
Reduction in Kinetic Energy
Repulsive Forces
Reduction in Kinetic Energy
The beginning of paragraph two helps guide our thinking for this question. We know that molecules stack nearly when temperatures are low and pressures are intermediate. Decreasing kinetic energy allows the molecules to remain closer together and for the attractive forces that are present to initiate the stacking process. Thus, the beginning of the stacking process depends on the reduction in kinetic energy.
Example Question #116 : Chemistry
The Ideal Gas Law is as follows:






A class of students began studying the Ideal Gas Law and how the Pressure and the Volume relate to one another. They took 20 moles of a sample gas and kept the room at a temperature of 300 Kelvin. They then used different sized containers of the gas to limit and expand the volume. At each different volume, they measure the pressure of the gas on its container. The table they made from their results is seen in table 1.
|
Temperature in Kelvin |
Pressure Measured in Pascals |
|
|
|
|
200 Kelvin |
16, 628 Pascals |
|
400 Kelvin |
33, 256 Pascals |
|
600 Kelvin |
49, 884 Pascals |
|
800 Kelvin |
66, 512 Pascals |
TABLE 1
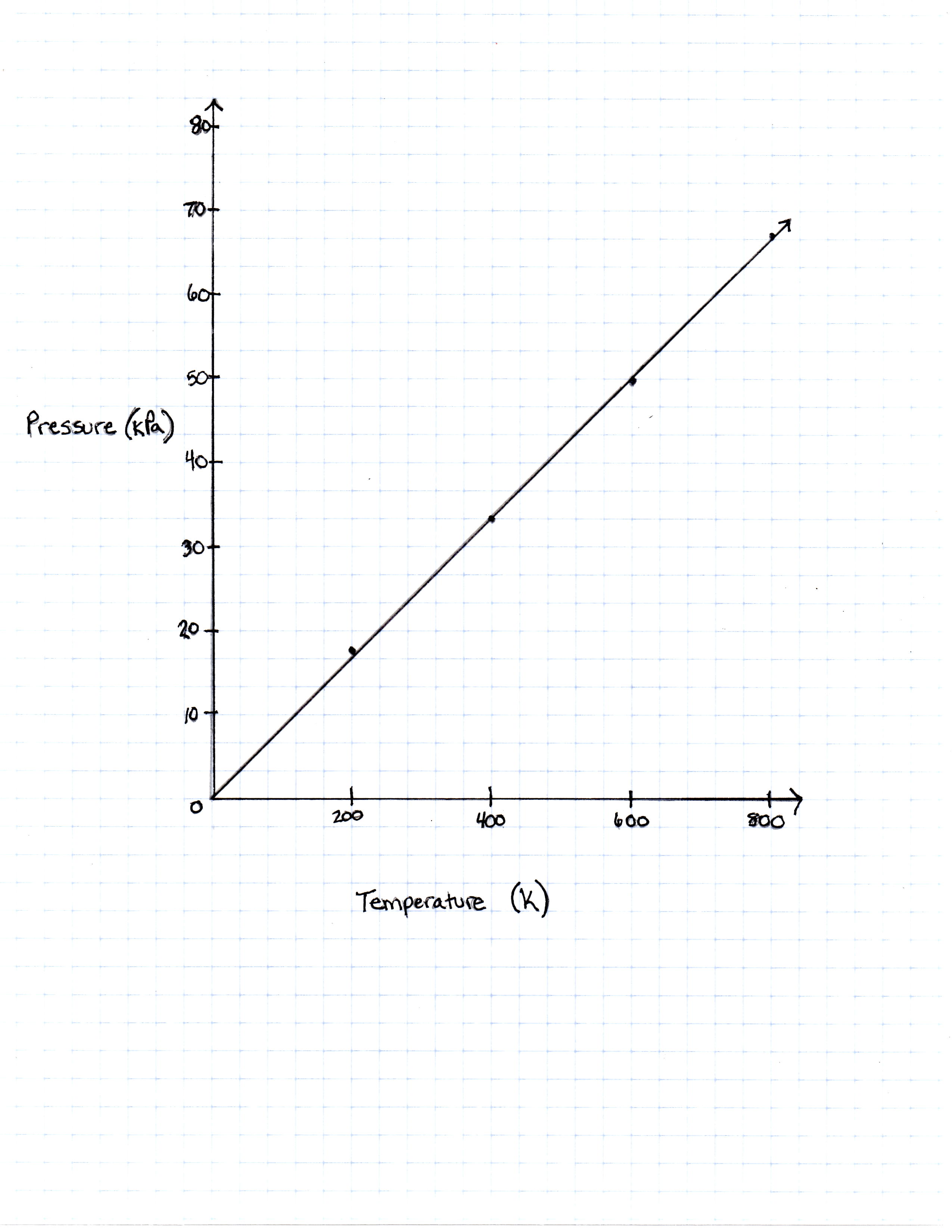
FIGURE 1
The graph the students made based on the data is seen in Figure 1.
Pressure is created by the movement of the gas molecules pushing against a container. 0 Kelvin is known as absolute 0, the temperature at which all molecule movement theoretically stops.
Will the pressure of a gas ever be 
Yes, but only if the theory holds true and the temperature reaches absolute 0 to stop all molecule movement.
Yes, but only if the temperature in Kelvin gets so high that the molecules move fast enough to explode their container.
No, because gas molecules' movement does not relate to temperature.
No, because the plots on the graph do not support the theory of absolute zero.
Yes, but only if Kelvin is converted to Celsius since water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius.
Yes, but only if the theory holds true and the temperature reaches absolute 0 to stop all molecule movement.
The plots on the graph as well as the equation of the Ideal Gas Law do support the idea that when temperature is equal to zero, so is pressure.
Example Question #117 : Chemistry
The Ideal Gas Law is as follows:





A class of students began studying the Ideal Gas Law and how the Pressure and the Volume relate to one another. They took 20 moles of a sample gas and kept the room at a temperature of 300 Kelvin. They then used different sized containers of the gas to limit and expand the volume. At each different volume, they measure the pressure of the gas on its container. The table they made from their results is seen in table 1.
|
Temperature in Kelvin |
Pressure Measured in Pascals |
|
|
|
|
200 Kelvin |
16, 628 Pascals |
|
400 Kelvin |
33, 256 Pascals |
|
600 Kelvin |
49, 884 Pascals |
|
800 Kelvin |
66, 512 Pascals |
TABLE 1

FIGURE 1
The graph the students made based on the data is seen in Figure 1.
Pressure is created by the movement of the gas molecules pushing against a container. 0 Kelvin is known as absolute 0, the temperature at which all molecule movement theoretically stops.
What would the pressure be if the temperature of the gas was increased to 273 Kelvin?
The answer cannot be determined from the equation
The Ideal Gas Law is given with pressure measured in Pascals. If the number 273 Kelvin was plugged into the equation, the number of Pascals that would be 
![P=[(8.314)(20)/2]273 = 22,697.22](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/84982/gif.latex)
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ACT Science Resources










