All ACT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Hexagon
What is the side of a Hexagon whose area is 
To find the side of a hexagon given the area, set the area formula equal to the given area and solve for the side.
Example Question #41 : Geometry
The sum of all the angles inside of a regular hexagon is 
In a regular hexagon, all of the sides are the same length, and all of the angles are equivalent. The problem tells us that all of the angles inside the hexagon sum to 



Example Question #44 : Geometry
All of the angles marked are exterior angles.
What is the value of 
There are two key things for a question like this. The first is to know that a polygon has a total degree measure of:


Therefore, a hexagon like this one has:

Next, you should remember that all of the exterior angles listed are supplementary to their correlative interior angles. This lets you draw the following figure:

Now, you just have to manage your algebra well. You must sum up all of the interior angles and set them equal to 



Simplify and solve for 
This is 

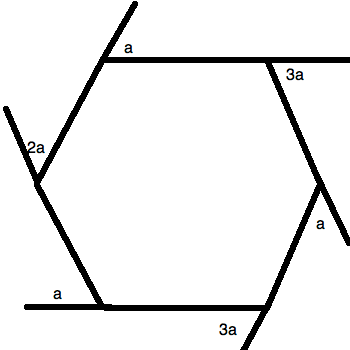
Example Question #45 : Geometry

The figure above is a hexagon. All of the angles listed (except the interior one) are exterior angles to the hexagon's interior angles.
What is the value of 
There are two key things for a question like this. The first is to know that a polygon has a total degree measure of:


Therefore, a hexagon like this one has:

Next, you should remember that all of the exterior angles listed are supplementary to their correlative interior angles. This lets you draw the following figure:

Now, you just have to manage your algebra well. You must sum up all of the interior angles and set them equal to 
Solve for 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Hexagon
A hexagon is made up of 6 congruent equilateral triangles. Each equilateral triangle has a length of 8 units. What is the area in square units of the hexagon?
First, let's draw out the hexagon.

Because the hexagon is made up of 6 equilateral triangles, to find the area of the hexagon, we will first find the area of each equilateral triangle then multiply it by 6.

Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we find that the height of each equilateral triangle is 
The area of the triangle is then
Multiply this value by 6 to find the area of the hexagon.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Hexagon
What is the area of a regular hexagon with a side length of 
This question is asking about the area of a regular hexagon that looks like this:

Now, you could proceed by noticing that the hexagon can be divided into little equilateral triangles:

By use of the properties of isosceles and 




It is likely easiest merely to memorize the aforementioned equation for the area of an equilateral triangle. From this, you can derive the hexagon area equation mentioned above. Using this equation and our data, we know:
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Area Of A Hexagon

The figure above is a regular hexagon. 
What is the area of the figure above?
You can redraw the figure given to notice the little equilateral triangle that is formed within the hexagon. Since a hexagon can have the 



Now, the 




We know, then, that:
Another way to write 
Now, there are several ways you could proceed from here. Notice that there are 
and for your data...
The area of the whole figure is:

Example Question #4 : How To Find The Area Of A Hexagon
What is the area of a regular hexagon with a perimeter of 
A hexagon has 


This question is asking about the area of a regular hexagon that looks like this:

Now, you could proceed by noticing that the hexagon can be divided into little equilateral triangles:

By use of the properties of isosceles and 




It is likely easiest merely to memorize the aforementioned equation for the area of an equilateral triangle. From this, you can derive the hexagon area equation mentioned above. Using this equation and our data, we know:
Example Question #5 : How To Find The Area Of A Hexagon
What is the area of a regular hexagon with a side length of 


For a hexagon with side length 

We have a side length of 4 miles, so we plug that into the equation and simplify the fraction.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Hexagon
What is the area of a hexagon with a side of length two? Simplify all fractions and square roots.
To find the area of a hexagon with a given side length, 
Plugging in 2 for 

All ACT Math Resources













































































