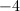All ACT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find Out When An Equation Has No Solution
Given the following system, find the solution:
x = y – 2
2x – 2y = 2
(0, 1)
no solution
(1, 1)
(0, 0)
(1, 2)
no solution
When 2 equations in a system have the same slopes, they will either have no solution or infinite solutions. Since the y-intercepts are not the same, there is no solution to this system.
Example Question #2 : How To Find Out When An Equation Has No Solution
Solve for 
Infinite Solutions
No solution
No solution
Like other "solve for x" problems, to begin it, the goal is to get x by itself on one side of the equals sign. In this problem, before doing so, the imaginary -1 in front of (-27x+27) must be distributed.
Once this is done, you may start to try to get x by itself.
However, when subtracting 27x from either side and doing the same on the other, the 27x term cancels out. As a result, the equation becomes:
We know this is an untrue statement because these numbers are 5 spaces away from each other on the number line. The final answer is No Solution.
Example Question #3 : How To Find Out When An Equation Has No Solution
Given the following system, find the solution:
No solution
No solution
When two equations have the same slope, they will have either no solution or infinite solutions. By putting both equations into the form 
and
With the equations in this form, we can see that they have the same slope, but different y-intercepts. Therefore, there is no solution to this system.
Example Question #2 : How To Find Out When An Equation Has No Solution
Solve the following equation for 
No solution
Infinite solutions
No solution
In order to solve for 

First, we can distribute the 

When we try to get 

We know this is an untrue statement, so there is no solution to this equation.
Example Question #71 : Equations / Inequalities
Find the solution to the following equation if x = 3:
y = (4x2 - 2)/(9 - x2)
6
0
3
no possible solution
no possible solution
Substituting 3 in for x, you will get 0 in the denominator of the fraction. It is not possible to have 0 be the denominator for a fraction so there is no possible solution to this equation.
Example Question #2 : Linear / Rational / Variable Equations
–1/2
There is no solution
–3
3
1
There is no solution
Example Question #72 : Equations / Inequalities

None of the other answers
A fraction is considered undefined when the denominator equals 0. Set the denominator equal to zero and solve for the variable.
Example Question #1 : How To Find Out When An Equation Has No Solution


No solutions.
No solutions.
Cross multiplying leaves 
Example Question #1 : How To Find Out When An Equation Has No Solution
I. x = 0
II. x = –1
III. x = 1
I only
II only
II and III only
III only
I, II, and III
I only
Example Question #141 : Linear / Rational / Variable Equations
Solve:
First, distribute, making sure to watch for negatives.
Combine like terms.
Subtract 7x from both sides.
Add 18 on both sides and be careful adding integers.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ACT Math Resources