All Trigonometry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #5 : Graphing Sine And Cosine
Let 

The 3 in the function above affects what attribute of the graph of 
Period
Phase shift
Vertical shift
Amplitude
Vertical shift
The period of the function is indicated by the coefficient in front of 
The amplitude of the function is given by the coefficient in front of the 
The phase shift is given by the value being added or subtracted inside the 

The only unexamined attribute of the graph is the vertical shift, so 3 is the vertical shift of the graph.
Example Question #2 : Graphing Sine And Cosine

What is an equation for the above function, enlarged below?

The amplitude of a sinusoidal function is 


The graph moves through the origin, so it is either a sine or a shifted cosine graph.
It repeats once in every 


The only answer in which both the correct amplitude and period is found is:
Example Question #1 : Graphing Sine And Cosine
What is the domain of the sine function? What is the domain of the cosine function?
Domain of sine:
Domain of cosine:
Domain of sine:
Domain of cosine: all real numbers
Domain of sine: all real numbers
Domain of cosine: all real numbers
Domain of sine: all real numbers
Domain of cosine:
Domain of sine: all real numbers
Domain of cosine: all real numbers
Both sine and cosine functions go on infinitely to the left and right when viewed on a graph. For this reason, each of these functions has domains of "all real numbers."
Alternatively, each of these functions ranges between -1 and 1 in the y direction. The incorrect answers all include ![[-1,1]](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1173745/gif.latex)
Example Question #2 : Graphing Sine And Cosine
Which of the following would correctly translate the function 

Shift 
Shift 
Shift 

Shift 

Shift 

Shift 

The graph of 








Example Question #9 : Graphing Sine And Cosine
Which of the following graphs represents the function 




The graph of 

This graph goes through three transformations. First, take the graph of 

Finally, we need to shift the graph up 1 unit. This is represented by the black graph, below.

The incorrect answers display the graphs of the functions 


Example Question #23 : Trigonometric Graphs
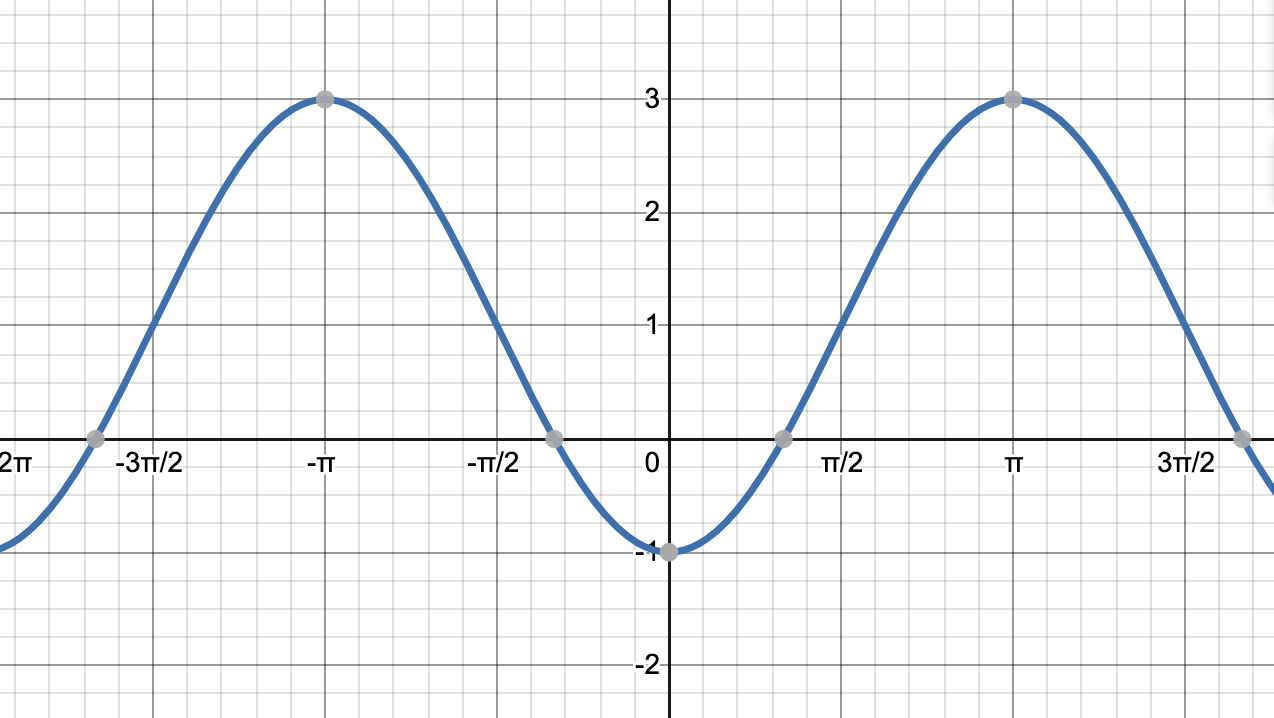
Give the equation of the following graph.

Looking at our graph, we can tell that the period is 




This eliminates one answer choice. We then retrun to our graph and see that the amplitude is 3. Remembering that the amplitude is the number in front of the function, we can eliminate two more choices.
We then examine our graph and realize it contains the point 
Example Question #1 : Graphing Secant And Cosecant
This is the graph of what function of x?




Example Question #141 : Trigonometry
Which of the following is the graph of 





In order to graph 



Now anywhere this graph crosses the x-axis a vertical asymptote will form for the 




And then we are left with the graph of 

Example Question #21 : Trigonometric Graphs
Considering the general form of the cosecant transformation function 
A = Amplitude , 
A = Amplitude , B = Period , C = Phase Shift, D = Vertical Shift
A = Phase Shift , B = Period , C = Amplitude, D = Vertical Shift
A = Amplitude , 
A = Amplitude , 
Since cosecant is a reciprocal of sine, it uses the same general formula of the sine function with the letters corresponding to the same transformations. Note that while A does correspond to amplitude, the cosecant function extends infinitely upwards and downwards so there is no amplitude for the graphs.
Example Question #5 : Graphing Secant And Cosecant
Which of the following is the graph of 




Knowing that the graph of 

we can use the general form of the cosecant transformation equation, 



Period =
Period =
Period =





Lastly, we must apply the transformation for 

The application of these transformations leaves us with our graph of 

All Trigonometry Resources







![[-1,1]](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1173733/gif.latex)
![[-1,1]](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1173734/gif.latex)
![[-1,1]](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1173735/gif.latex)
![[-1,1]](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1173736/gif.latex)



















