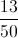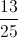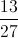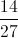All SSAT Middle Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find Length Of A Line
The coordinates of 




A rectangle has two diagonals with the same length. So we should find the length of 
Example Question #1 : How To Find Length Of A Line
If a circle has a radius of 12 inches, the biggest line that would be drawn within the circle is:
The largest line that can be drawn within a circle is the diamater. The diameter is equal to twice the radius. Given that the radius is equal to 12 inches, the largest line that could be drawn (the diameter) would be equal to 24 inches.
Example Question #11 : How To Find Length Of A Line
The diameter of a circle is 


By definition, the radius 

Plugging in 

Since the question is asking us for the value of 

Example Question #1 : Data Analysis And Probability
A pair of fair dice are rolled. What is the probability that the sum will be a multiple of 3?
There are four possible multiples of 3 that can come out: 3,6,9, and 12. There are 36 equally probable outcomes; the following will result in a multiple of 3:
These are 12 outcomes out of 36, making the probability
Example Question #1 : Data Analysis And Probability
A pair of fair dice are rolled. What is the probability that the sum will be a multiple of 4?
There are three possible multiples of 4 that can come out: 4, 8, and 12. There are 36 equally probable outcomes; the following will result in a multiple of 4:
These are 9 outcomes out of 36, making the probability
Example Question #1 : Outcomes
Some balls are placed in a hat - ten red, four blue, six yellow. What is the probability that a randomly drawn ball will not be blue?
There are 20 balls in the hat. All but four - that is, sixteen - are blue, so the probability of a draw resulting in a non-blue ball is
Example Question #2 : Outcomes
The red jacks are removed from a standard deck of fifty-two cards. What is the probability that a card randomly drawn from that modified deck will be black?
The removal of two red jacks - and no black cards - results in there being fifty cards, twenty-six of them black. Therefore, the probability of a randomly drawn card being black is 
Example Question #3 : Outcomes
A standard deck of cards is modified by adding the red threes from another deck. What is the probability that a card randomly drawn from that modified deck will be a red card?
The addition of two red threes from another deck results in the deck comprising fifty-four cards, twenty-eight of which are red. Therefore, the probability of a randomly drawn card being red is
Example Question #4 : Outcomes
A standard deck of cards is modified by adding the red queens from another deck. What is the probability that a card randomly drawn from that modified deck will be a face card (jack, queen, king)?
There are four cards of each rank in a standard deck; since three ranks - jacks, queens, kings - are considered face cards, this makes twelve face cards out of the fifty-two. But two more face cards - two red queens - have been introduced, so now there are fourteen face cards out of fifty-four. This makes the probability of a randomly drawn card being a face card
Example Question #5 : Outcomes
In a bag of marbles, there are 


3
The probability of drawing a blue marble on the first try is 





.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Middle Level Math Resources