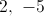All SAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Exponents And The Distributive Property
Factor 2x2 - 5x – 12
(x + 4) (2x + 3)
(x + 4) (2x + 3)
(x - 4) (2x + 3)
(x – 4) (2x – 3)
(x - 4) (2x + 3)
Via the FOIL method, we can attest that x(2x) + x(3) + –4(2x) + –4(3) = 2x2 – 5x – 12.
Example Question #572 : Algebra
x > 0.
Quantity A: (x+3)(x-5)(x)
Quantity B: (x-3)(x-1)(x+3)
Quantity B is greater
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given
The two quantities are equal
Quantity A is greater
Quantity B is greater
Use FOIL:
(x+3)(x-5)(x) = (x2 - 5x + 3x - 15)(x) = x3 - 5x2 + 3x2 - 15x = x3 - 2x2 - 15x for A.
(x-3)(x-1)(x+3) = (x-3)(x+3)(x-1) = (x2 + 3x - 3x - 9)(x-1) = (x2 - 9)(x-1)
(x2 - 9)(x-1) = x3 - x2 - 9x + 9 for B.
The difference between A and B:
(x3 - 2x2 - 15x) - (x3 - x2 - 9x + 9) = x3 - 2x2 - 15x - x3 + x2 + 9x - 9
= - x2 - 4x - 9. Since all of the terms are negative and x > 0:
A - B < 0.
Rearrange A - B < 0:
A < B
Example Question #2 : Exponents And The Distributive Property
Solve for all real values of 
First, move all terms to one side of the equation to set them equal to zero.
All terms contain an 
Now, we can factor the quadratic in parenthesis. We need two numbers that add to 

We now have three terms that multiply to equal zero. One of these terms must equal zero in order for the product to be zero.
Our answer will be 
Example Question #1 : Exponents And The Distributive Property
Find the product in terms of 
This question can be solved using the FOIL method. So the first terms are multiplied together:
This gives:
The x-squared is due to the x times x.
The outer terms are then multipled together and added to the value above.
The inner two terms are multipled together to give the next term of the expression.
Finally the last terms are multiplied together.
All of the above terms are added together to give:
Combining like terms gives

Example Question #1 : How To Use Foil
Expand the following expression:
Expand the following expression:
Let's begin by recalling the meaning of FOIL: First, Outer, Inner, Last.
This means that in a situation such as we are given here, we need to multiply all the terms in a particular way. FOIL makes it easy to remember to multiply each pair of terms.
Let's begin:
First:
Outer:
Inner:
Last:
Now, put it together in standard form to get:
Example Question #1 : How To Use Foil With Exponents
If 

Take the square root of both sides.
Add 3 to both sides of each equation.
Example Question #2 : How To Use Foil With Exponents
Simplify:
= x3y3z3 + x2y + x0y0 + x2y
= x3y3z3 + x2y + 1 + x2y
= x3y3z3 + 2x2y + 1
Example Question #3 : How To Use Foil With Exponents
Use the FOIL method to simplify the following expression:
Use the FOIL method to simplify the following expression:
Step 1: Expand the expression.
Step 2: FOIL
First:
Outside:
Inside:
Last:
Step 2: Sum the products.
Example Question #6 : How To Use Foil With Exponents
Square the binomial.
We will need to FOIL.
First:
Inside:
Outside:
Last:
Sum all of the terms and simplify.
Example Question #1 : How To Use Foil With Exponents
Which of the following is equivalent to 4c(3d)3 – 8c3d + 2(cd)4?
cd(54c * d3 – 4c3 + c2 * d2)
2(54d2 – 4c2 + 2c3 * d3)
2cd(54d2 – 4c2 + c3 * d3)
None of the other answers
2cd(54d2 – 4c2 + c3 * d3)
First calculate each section to yield 4c(27d3) – 8c3d + 2c4d4 = 108cd3 – 8c3d + 2c4d4. Now let's factor out the greatest common factor of the three terms, 2cd, in order to get: 2cd(54d2 – 4c2 + c3d3).
All SAT Math Resources