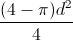All SAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #61 : Circles
If the radius of Circle A is three times the radius of Circle B, what is the ratio of the area of Circle A to the area of Circle B?
3
6
9
12
15
9
We know that the equation for the area of a circle is π r2. To solve this problem, we pick radii for Circles A and B, making sure that Circle A’s radius is three times Circle B’s radius, as the problem specifies. Then we will divide the resulting areas of the two circles. For example, if we say that Circle A has radius 6 and Circle B has radius 2, then the ratio of the area of Circle A to B is: (π 62)/(π 22) = 36π/4π. From here, the π's cancel out, leaving 36/4 = 9.
Example Question #541 : Plane Geometry
- A circle is inscribed inside a 10 by 10 square. What is the area of the circle?
50π
40π
100π
10π
25π
25π
Area of a circle = A = πr2
R = 1/2d = ½(10) = 5
A = 52π = 25π
Example Question #382 : Geometry
A square has an area of 1089 in2. If a circle is inscribed within the square, what is its area?
1089π in2
272.25π in2
33 in2
33π in2
16.5 in2
272.25π in2
The diameter of the circle is the length of a side of the square. Therefore, first solve for the length of the square's sides. The area of the square is:
A = s2 or 1089 = s2. Taking the square root of both sides, we get: s = 33.
Now, based on this, we know that 2r = 33 or r = 16.5. The area of the circle is πr2 or π16.52 = 272.25π.
Example Question #61 : Circles
A square has an area of 32 in2. If a circle is inscribed within the square, what is its area?
32π in2
16π in2
2√2 in2
4√2 in2
8π in2
8π in2
The diameter of the circle is the length of a side of the square. Therefore, first solve for the length of the square's sides. The area of the square is:
A = s2 or 32 = s2. Taking the square root of both sides, we get: s = √32 = √(25) = 4√2.
Now, based on this, we know that 2r = 4√2 or r = 2√2. The area of the circle is πr2 or π(2√2)2 = 4 * 2π = 8π.
Example Question #382 : Psat Mathematics
A manufacturer makes wooden circles out of square blocks of wood. If the wood costs $0.25 per square inch, what is the minimum waste cost possible for cutting a circle with a radius of 44 in.?
1936 – 484π dollars
1936π dollars
5808 dollars
7744 – 1936π dollars
1936 dollars
1936 – 484π dollars
The smallest block from which a circle could be made would be a square that perfectly matches the diameter of the given circle. (This is presuming we have perfectly calibrated equipment.) Such a square would have dimensions equal to the diameter of the circle, meaning it would have sides of 88 inches for our problem. Its total area would be 88 * 88 or 7744 in2.
Now, the waste amount would be the "corners" remaining after the circle was cut. The area of the circle is πr2 or π * 442 = 1936π in2. Therefore, the area remaining would be 7744 – 1936π. The cost of the waste would be 0.25 * (7744 – 1936π). This is not an option for our answers, so let us simplify a bit. We can factor out a common 4 from our subtraction. This would give us: 0.25 * 4 * (1936 – 484π). Since 0.25 is equal to 1/4, 0.25 * 4 = 1. Therefore, our final answer is: 1936 – 484π dollars.
Example Question #383 : Psat Mathematics
A manufacturer makes wooden circles out of square blocks of wood. If the wood costs $0.20 per square inch, what is the minimum waste cost possible for cutting a circle with a radius of 25 in.?
2500 - 625π dollars
625 - 25π dollars
625 dollars
500 dollars
500 - 125π dollars
500 - 125π dollars
The smallest block from which a circle could be made would be a square that perfectly matches the diameter of the given circle. (This is presuming we have perfectly calibrated equipment.) Such a square would have dimensions equal to the diameter of the circle, meaning it would have sides of 50 inches for our problem. Its total area would be 50 * 50 or 2500 in2.
Now, the waste amount would be the "corners" remaining after the circle was cut. The area of the circle is πr2 or π * 252 = 625π in2. Therefore, the area remaining would be 2500 - 625π. The cost of the waste would be 0.2 * (2500 – 625π). This is not an option for our answers, so let us simplify a bit. We can factor out a common 5 from our subtraction. This would give us: 0.2 * 5 * (500 – 125π). Since 0.2 is equal to 1/5, 0.2 * 625 = 125. Therefore, our final answer is: 500 – 125π dollars.
Example Question #21 : How To Find The Area Of A Circle
25π
100π
50π
20π
10π
50π
Example Question #11 : Radius
A circle with diameter of length 
In order to find the area that is inside the square but outside the circle, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the square. The area of a circle is equal to 

Divide both sides by 2.
We will now substitute this into the formula for the area of the circle.
area of circle =
We next will need to find the area of the square. Because the circle is inscribed in the square, the diameter of the circle is equal to the length of the circle's side. In other words, the square has side lengths equal to d. The area of any square is equal to the square of its side length. Therefore, the area of the square is 
area of square =
Lastly, we will subtract the area of the circle from the area of the square.
difference in areas =
We will rewrite 
difference in areas =
The answer is 
Example Question #12 : How To Find The Area Of A Circle
An original circle has an area of 
The formula for the area of a circle is 

Example Question #31 : Radius
A square has an area of 
The area of a square is given by 


All SAT Math Resources