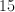All PSAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Geometry
In rectangle ABCD, both diagonals are drawn and intersect at point E.
Let the measure of angle AEB equal x degrees.
Let the measure of angle BEC equal y degrees.
Let the measure of angle CED equal z degrees.
Find the measure of angle AED in terms of x, y, and/or z.
180 – 1/2(x + z)
180 – 2(x + z)
180 – (x + y + z)
360 – x + y + z
180 – y
180 – 1/2(x + z)
Intersecting lines create two pairs of vertical angles which are congruent. Therefore, we can deduce that y = measure of angle AED.
Furthermore, intersecting lines create adjacent angles that are supplementary (sum to 180 degrees). Therefore, we can deduce that x + y + z + (measure of angle AED) = 360.
Substituting the first equation into the second equation, we get
x + (measure of angle AED) + z + (measure of angle AED) = 360
2(measure of angle AED) + x + z = 360
2(measure of angle AED) = 360 – (x + z)
Divide by two and get:
measure of angle AED = 180 – 1/2(x + z)
Example Question #782 : New Sat
A student creates a challenge for his friend. He first draws a square, the adds the line for each of the 2 diagonals. Finally, he asks his friend to draw the circle that has the most intersections possible.
How many intersections will this circle have?

Example Question #1 : Geometry
Two pairs of parallel lines intersect:

If A = 135o, what is 2*|B-C| = ?
180°
160°
170°
140°
150°
180°
By properties of parallel lines A+B = 180o, B = 45o, C = A = 135o, so 2*|B-C| = 2* |45-135| = 180o
Example Question #2 : Lines
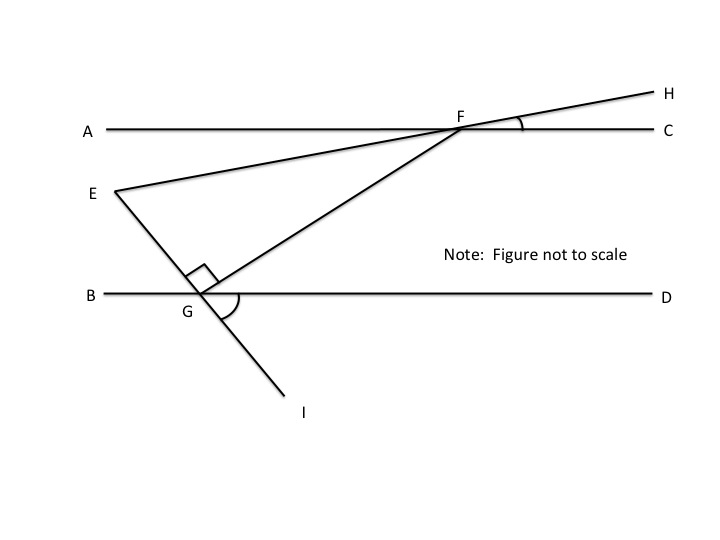
Lines 





Not enough information.
Since we know opposite angles are equal, it follows that angle 

Imagine a parallel line passing through point 




Example Question #1171 : High School Math
If 


When the measure of an angle is added to the measure of its supplement, the result is always 180 degrees. Put differently, two angles are said to be supplementary if the sum of their measures is 180 degrees. For example, two angles whose measures are 50 degrees and 130 degrees are supplementary, because the sum of 50 and 130 degrees is 180 degrees. We can thus write the following equation:
Subtract 40 from both sides.
Add 
The answer is 
Example Question #511 : Plane Geometry
In the following diagram, lines 



It cannot be determined
When two parallel lines are intersected by another line, the sum of the measures of the interior angles on the same side of the line is 180°. Therefore, the sum of the angle that is labeled as 100° and angle y is 180°. As a result, angle y is 80°.
Another property of two parallel lines that are intersected by a third line is that the corresponding angles are congruent. So, the measurement of angle x is equal to the measurement of angle y, which is 80°.
Example Question #11 : Lines
The measure of the supplement of angle A is 40 degrees larger than twice the measure of the complement of angle A. What is the sum, in degrees, of the measures of the supplement and complement of angle A?
90
50
140
190
40
190
Let A represent the measure, in degrees, of angle A. By definition, the sum of the measures of A and its complement is 90 degrees. We can write the following equation to determine an expression for the measure of the complement of angle A.
A + measure of complement of A = 90
Subtract A from both sides.
measure of complement of A = 90 – A
Similarly, because the sum of the measures of angle A and its supplement is 180 degrees, we can represent the measure of the supplement of A as 180 – A.
The problem states that the measure of the supplement of A is 40 degrees larger than twice the measure of the complement of A. We can write this as 2(90-A) + 40.
Next, we must set the two expressions 180 – A and 2(90 – A) + 40 equal to one another and solve for A:
180 – A = 2(90 – A) + 40
Distribute the 2:
180 - A = 180 – 2A + 40
Add 2A to both sides:
180 + A = 180 + 40
Subtract 180 from both sides:
A = 40
Therefore the measure of angle A is 40 degrees.
The question asks us to find the sum of the measures of the supplement and complement of A. The measure of the supplement of A is 180 – A = 180 – 40 = 140 degrees. Similarly, the measure of the complement of A is 90 – 40 = 50 degrees.
The sum of these two is 140 + 50 = 190 degrees.
Example Question #121 : Lines






None of the other answers









Example Question #11 : Intersecting Lines And Angles
Two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal. If the minor angle of intersection between the first parallel line and the transversal is 
When a line intersects two parallel lines as a transversal, it always passes through both at identical angles (regardless of distance or length of arc).
Example Question #12 : Lines
If 




122
148
32
62
58
148
The question states that 
The sum of angles of a triangle is equal to 180 degrees. The question states that 
Use this information to solve for the missing angle:
The degree measure of a straight line is 180 degrees; therefore, we can write the following equation:
The measure of 
Certified Tutor
All PSAT Math Resources