All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #571 : Organic Chemistry

What is the product of the given reaction?
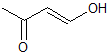





This is a basic Claisen condensation reaction in which the 
 .
.
The attack at the ester carbonyl leads to the leaving of 
Example Question #2 : Help With Ether And Ester Reactions
What is the product of the following reaction?


II and III
II only
I and II
IV only
II and III
Treatment of ethyl acetate with methoxide will yield the enolate ion (II). However, side trans-esterification reactions will also result in formation of product III.
Example Question #571 : Organic Chemistry

Which reagent may be used to convert a carboxylic acid to an acid chloride, as shown?
It is extremely useful in organic synthesis to utilize methods by which less reactive carboxylic acids (and their derivatives) may be converted to more reactive species, like acid chlorides. Such reactions are not always intuitive as they proceed by transforming low-energy species to more energetic states. Reagents such as thionyl chloride 

Example Question #1 : Help With Carboxylic Acid Reactions
Which of the following is derived from a carboxylic acid?
None of these
Imine
Aldehyde
Acid anhydride
Acid anhydride
A carboxylic acid can be synthesized directly into an acid anhydride by introducing the carboxylic acid to an acid chloride.
Example Question #11 : Carbonyl Reactants

What is the major product of the given reaction?





This question is asking us to determine what the product will be when a carboxylic acid is reacted with thionyl chloride, 


Example Question #1 : Help With Carboxylic Acid Reactions
What is the product of the reaction shown?


III
I
II
IV
III
The Grignard reagent also acts as a base, and will remove any protons that have a low-enough pKa. This means that the alpha hydrogen will be removed, and the resulting carboxylate ion is stabilized through resonance and is unlikely to react with the protonated Grignard reagent.
Example Question #12 : Carbonyl Reactants
What is the product of the reaction below?
This reaction is an acid-catalyzed esterification of a carboxylic acid. In the reaction the carbonyl is attacked by the alcohol oxygen, and the carbonyl is reformed by kicking off what was the hydroxyl group in the original carboxylic acid. What is left is an ester (of the form RCOOR', with R' containing the same number of carbons as was in the original alcohol).
Example Question #1 : Help With Alcohol Reactions
The compound below is reacted with 

The initially chiral carbon has an 




Example Question #582 : Organic Chemistry

What is the product of the reaction when the given molecule is introduced to an acidic solution?
4-bromo-2-hexene
None of these
2-bromo-4-hexene
2-bromo-4-hexanol
3-bromo-5-hexanol
4-bromo-2-hexene
In acidic solution, a hydrogen will be added to the hydroxy group of the given compound. This intermediate is a good leaving group. As it leaves, a hydrogen will be abstracted and a double bond will form. The bond is across carbons two and three becasue those two are more highly substituted than carbon 1, which is primary. The naming begins at the double bond, so the name is 4-bromo-2-hexene.
Example Question #19 : Carbonyl Reactants

Which reagent(s) would achieve the given synthetic transformation?
PCC
Chromic acid (formed in-situ via 



All Organic Chemistry Resources






![\xrightarrow[]{SOCl_{2}}\: ?](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/479869/gif.latex)