All NCLEX Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #8 : Circulatory System
Oxygen-poor blood flows from the __________ to the __________.
pulmonary veins . . . left atrium
pulmonary arteries . . . right atrium
vena cava . . . left atrium
vena cava . . . right atrium
vena cava . . . right atrium
Deoxygenated blood from the body flows through the superior and inferior vena cava into the right atrium of the heart. From there it enters the right ventricle, then is ejected into the lungs via the pulmonary arteries. The blood is oxygenated in the lungs, then flows through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, then into the left ventricle to be pumped back out into the body.
Example Question #9 : Circulatory System
How does parasympathetic innervation affect the heart?
Increases heart rate and decreases cardiac output
Slows heart rate and decreases cardiac output
Increases heart rate and increases cardiac output
Slows heart rate and increases cardiac output
Slows heart rate and decreases cardiac output
Sympathetic innervation will decrease the heart rate, which will automatically decrease the cardiac output
Example Question #11 : Circulatory System
Which of the following causes the S1 heart sound (lub)?
The closing of the aortic and pulmonary valves
The opening of the tricuspid and mitral (AV) valves
The opening of the aortic and pulmonary valves
The closing of the tricuspid and mitral (AV) valves
The closing of the tricuspid and mitral (AV) valves
The S1 heart sound (sometimes referred to as "lub") is caused by the sudden snapping-shut of the tricuspid and mitral valves during systole, when the heart contracts and tension on the chordae tendinae is released. No sound is produced on the opening of these or any other valves in the heart.
Example Question #11 : Heart
The contraction rate is set in what area of the heart?
The bundle of His
The Purkinje fibers
The atrioventricular node
The sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node
The contraction rate for the heart is set by the cells of the sinoatrial node, also known as the pacemaker cells of the heart. These cells have membranes that are especially permeable to ions, and are able to depolarize on their own at a rate of 70-100 beats per minute. All the other areas listed do have their own spontaneous contractility, but their rates are slower than that of the sinoatrial node. Thus, the sinoatrial node is the pacemaker in a healthy heart.
Example Question #41 : Circulatory And Respiratory Systems
Which of the following is the proper unit of measurement for blood pressure?
IU
The proper unit when recording a patient's blood pressure is mmHg, or millimeter of mercury. This is derived from a historical measurement of how many millimeters of mercury in a mercury manometer were able to be elevated by a particular pressure. Due to it's toxicity, are longer used in medical equipment, though the 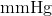
Example Question #41 : Circulatory And Respiratory Systems
A patient has a 49 year history of hypertension. Which part of the heart would be most enlarged on echocardiogram?
Left ventricle
Pulmonary artery
Left atrium
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
The left ventricle is the most commonly enlarged heart structure seen in chronic hypertension. The left ventricle must overcome the afterload of the arterial system by becoming hypertrophied. As a result, the heart gets remodeled to overcome the systemic high blood pressures. The left ventricle directly pumps blood from the heart to the systemic circuit.
Example Question #1 : Lymphatic System
What organ of the lymphatic system is the site of T-cell maturation?
The lymph nodes
The spleen
The cisterna chyli
The thymus
The thymus
T-cell maturation occurs in the thymus, a small organ located in the upper part of the mediastinum, between the heart and the sternum. Mature T cells then may either circulate in the lymph or blood or reside in lymph nodes. The spleen is not a site of T cell maturation, though it does have other important immune functions, such as the production of antibodies and the removal of antibody-coated pathogens. The cisterna chyli is a part of the lymphatic system that is involved in lipid digestion.
Example Question #11 : Circulatory System
Digestive fat is absorbed through what specialized lymphatic vessels of the small intestine?
Lacteals
The cisterna chyli
Microvilli
Villi
Lacteals
Dietary fat is absorbed via lacteals, small lymph vessels contained within the body of the intestinal villi. Microvilli, tiny projections covering the surface of the villi, help with the absorption of minerals, vitamins, and other micronutrients. The cisterna chyli is a dilated pouch at the lower end of the thoracic duct that serves as a collection point for fatty chyle from the intestinal lacteals.
Example Question #3 : Lymphatic System
Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system?
Secondary gas exchange
Absorption and transportation of dietary fats
Lymphocyte transport and activation
Draining of interstitial fluid from tissues
Secondary gas exchange
The lymphatic system has several roles in the body, including drainage of interstitial fluid from tissues, transportation and activation of lymphocytes, and absorption and transportation of dietary fats. Red blood cells, however, are unable to enter lymph vessels, and so the lymphatic system does not participate in any type of gas exchange.
Example Question #641 : Nclex
All NCLEX Resources








