All MCAT Physical Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #691 : Mcat Physical Sciences
Hypothetically, if calcium hydroxide, lithium hydroxide, and potassium hydroxide all had a 

The solubilities of all three compounds are equal
Solubility is the ability of a solute to dissolve into a solvent. It is calculated by creating an equilibrium equation and solving for the concentration of dissolved ions.
For this question, we will need to set up equilibrium constant equations for each compound.
Note that the solid compounds are not included in the equilibrium expressions. Now we can work on finding the solubilities. For each mole of calcium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of calcium ions and two moles of hydroxide ions are released. For each mole of lithium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of lithium ions and one mole of hydroxide ions are released. For each mole of potassium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of potassium ions and one mole of hydroxide ions are released. Mathematically, we can equate these ratios to the ion concentrations in the equilibrium calculations.
In these calculations, 

Calcium hydroxide has the greatest solubility.
Example Question #21 : Solution Chemistry
The solubility product constant of 

Solubility is the ability of a solute to dissolve into a solvent. It is calculated by creating an equilibrium equation and solving for the concentration of dissolved ions.
For this question, we will need to set up the equilibrium constant equation for calcium hydroxide.
Note that the solid compound is not included in the equilibrium expression. Now we can work on finding the solubility. For each mole of calcium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of calcium ions and two moles of hydroxide ions are released. Mathematically, we can equate this ratio to the ion concentrations in the equilibrium calculation.
In this calculation, 

Example Question #11 : Analyzing Solids
How many moles of fluoride ions are present in 
Recall that the solubility product constant is given by the equation below, for a reaction in the following format.
Using our balanced reaction, we can find the solubility product equation for the dissociation of lead (II) fluoride.
For each molecule of lead (II) fluoride that dissolves, it produces one lead ion and two fluoride ions. We can conclude that the concentration of fluoride ions in solution will be twice the concentration of lead ions.
Use these variables in the solubility product equation, along with the given value from the question.
Now we can solve for the value of 
Remember that this value is equal to the concentration of lead ions in solution and half the concentration of fluoride ions in solution.
Example Question #163 : General Chemistry
Which of the following is true regarding the solubility product constant, 
The concentration of substance 
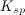
As more of substance 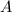


To determine the solubility product constant, we only need the concentrations and coefficients of the ions. The effective concentration of any pure substance (solid, liquid, or gas) is equal to one by definition, so does not influence the value of 
The units of the solubility product constant will depend on the coefficients of the products. 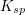
Example Question #11 : Solubility And Solution Equilibrium
Which of the following will not increase the solubility of a solution?
Decreasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent
All of these will increase solubility
Increasing the temperature of a solid solute in a liquid solvent
Increasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent
Increasing the pressure of a gas solute in a liquid solvent
Increasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent
Increasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent will decrease solubility. While dissolved, the gas is in equilibrium with the liquid. Adding heat will push the equilibrium in favor of the gas, causing it to precipitate from solution in the form of bubbles.
Increasing the pressure of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, decreasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, and increasing the temperature of a solid solute in a liquid solvent will all increase the solubility.
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Physical Resources





![Ca(OH)_2\rightleftharpoons Ca^{2+}+2OH^-;\ K_{sp}=[Ca^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/113712/gif.latex)
![LiOH\rightleftharpoons Li^++OH^-;\ K_{sp}=[Li^+][OH^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/100505/gif.latex)
![KOH\rightleftharpoons K^++OH^-;\ K_{sp}=[K^+][OH^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/113713/gif.latex)











![Ca(OH)_2\rightleftharpoons Ca^{2+}+2OH^-;\ K_{sp}=[Ca^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/100585/gif.latex)










![K_{sp}=[C]^c[D]^d](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/126068/gif.latex)

![K_{sp}=[Pb^{2+}][F^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1053245/gif.latex)
![[Pb^{2+}] = x](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/102001/gif.latex)
![[F^-]=2x](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/126071/gif.latex)


![x = \sqrt[3]{\frac{3.7*10^{-8}}{4}}=2.1*10^{-3}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/126073/gif.latex)
![[Pb^{2+}]=x=2.1*10^{-3}M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/102004/gif.latex)
![[F^-]=2x=2(2.1*10^{-3}M)=4.2*10^{-3}M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1051540/gif.latex)

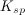
![K_{sp}=[C]^c[D]^d](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/73718/gif.latex)
![K_{sp}=[C]^c[D]^d](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/100575/gif.latex)



